15.1. Proprietà raster¶
Per visualizzare e impostare le proprietà di un layer raster, fai doppio clic sul nome del layer nella legenda della mappa, oppure fai clic con il tasto destro del mouse sul nome del layer e scegli Proprietà dal menu contestuale. In questo modo si aprirà la finestra di dialogo Proprietà layer
Ci sono diverse schede nella finestra di dialogo:
Suggerimento
Aggiornamenti in tempo reale
The Pannello Stile Layer provides you with some of the common features of the Layer properties dialog and is a good modeless widget that you can use to speed up the configuration of the layer styles and view your changes on the map canvas.
Nota
Because properties (symbology, label, actions, default values, forms…) of embedded layers (see Progetti nidificati) are pulled from the original project file, and to avoid changes that may break this behavior, the layer properties dialog is made unavailable for these layers.
15.1.1. Proprietà Informazioni¶
The  Information tab is read-only and represents
an interesting place to quickly grab summarized information and
metadata for the current layer.
Provided information are:
Information tab is read-only and represents
an interesting place to quickly grab summarized information and
metadata for the current layer.
Provided information are:
in base alla fonte dati del layer (formato di memorizzazione, percorso, tipo di dati, estensione, larghezza/altezza, compressione, dimensione dei pixel, statistiche sulle bande, numero di colonne, numero di righe e valore per nessun dato del raster….);
picked from the provided metadata: access, links, contacts, history… as well as dataset information (CRS, Extent, bands…).
15.1.2. Proprietà Sorgente¶
La scheda  Sorgente mostra le informazioni di base sul raster selezionato, inclusi:
Sorgente mostra le informazioni di base sul raster selezionato, inclusi:
Il Nome layer da visualizzare nel Pannello Layer;
the Coordinate Reference System: Displays the layer’s Coordinate Reference System (CRS). You can change the layer’s CRS, by selecting a recently used one in the drop-down list or clicking on the
 Select CRS button (see Scelta del sistema di riferimento delle coordinate).
Use this process only if the layer CRS is a wrong or not specified.
If you wish to reproject your data, use a reprojection algorithm
from Processing or
Save it as new dataset.
Select CRS button (see Scelta del sistema di riferimento delle coordinate).
Use this process only if the layer CRS is a wrong or not specified.
If you wish to reproject your data, use a reprojection algorithm
from Processing or
Save it as new dataset.
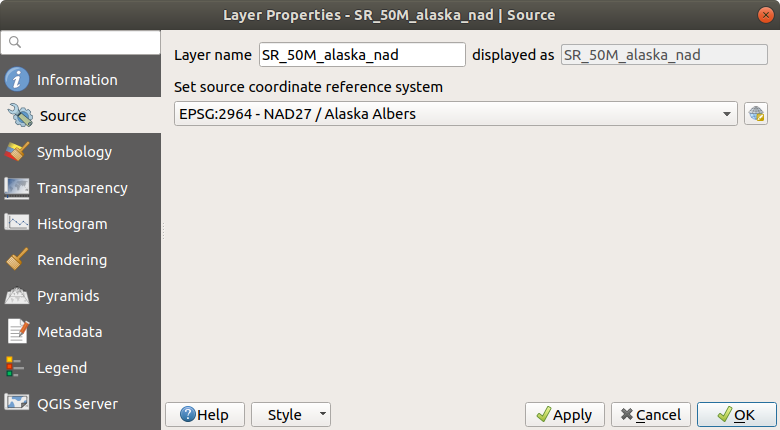
Fig. 15.1 Raster Layer Properties - Source Dialog¶
15.1.3. Proprietà Simbologia¶
15.1.3.1. Visualizzazione banda¶
QGIS offers four different Render types. The choice of renderer depends on the data type.
Multiband color - if the file comes with several bands (e.g. a satellite image with several bands).
Paletted/Unique values - for single band files that come with an indexed palette (e.g. a digital topographic map) or for general use of palettes for rendering raster layers.
Singleband gray - (one band of) the image will be rendered as gray. QGIS will choose this renderer if the file is neither multiband nor paletted (e.g. a shaded relief map).
Singleband pseudocolor - this renderer can be used for files with a continuous palette or color map (e.g. an elevation map).
Hillshade - Crea una ombreggiatura da una banda.
15.1.3.1.1. Colori Banda Multipla¶
With the multiband color renderer, three selected bands from the image will be used as the red, green or blue component of the color image. QGIS automatically fetches Min and Max values for each band of the raster and scales the coloring accordingly. You can control the value ranges in the Min/Max Value Settings section.
A Contrast enhancement method can be applied to the values: “No enhancement”, “Stretch to MinMax”, “Stretch and clip to MinMax” and “Clip to min max”.
Nota
Miglioramento contrasto
When adding GRASS rasters, the option Contrast enhancement will always be set automatically to stretch to min max, even if this is set to another value in the QGIS general options.
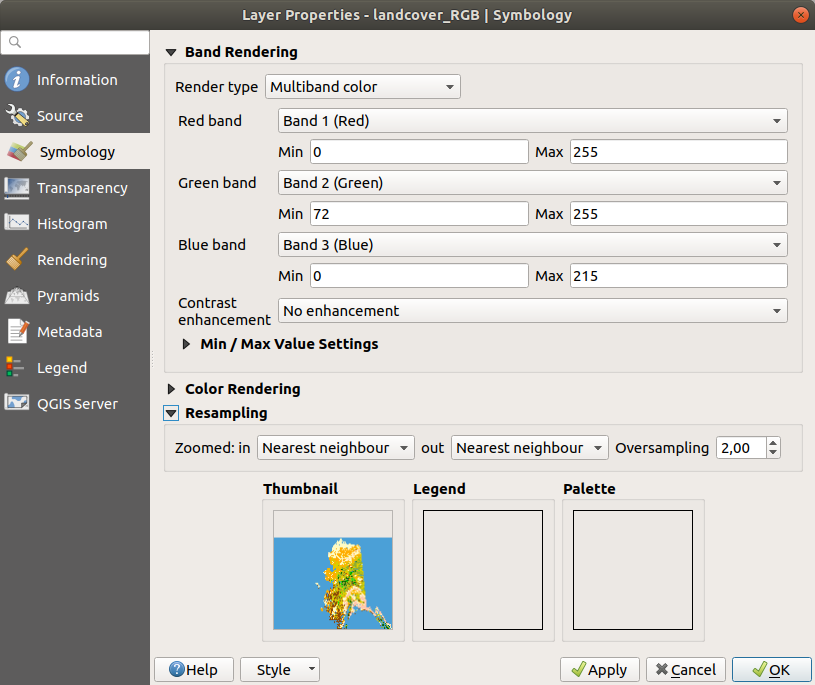
Fig. 15.2 Simbologia Raster - Visualizzazione colore multibanda¶
Suggerimento
Visualizzare una singola banda di un raster multibanda
If you want to view a single band of a multiband image (for example, Red), you might think you would set the Green and Blue bands to Not Set. But the preferred way of doing this is to set the image type to Singleband gray, and then select Red as the Gray band to use.
15.1.3.1.2. Valori a tavolozza/Univoci¶
This is the standard render option for singleband files that include a color table, where a certain color is assigned to each pixel value. In that case, the palette is rendered automatically.
It can be used for all kinds of raster bands, assigning a color to each unique raster value.
If you want to change a color, just double-click on the color and the Select color dialog appears.
It is also possible to assign labels to the colors. The label will then appear in the legend of the raster layer.
Right-clicking over selected rows in the color table shows a contextual menu to:
Change Color… for the selection
Change Opacity… for the selection
Change Label… for the selection
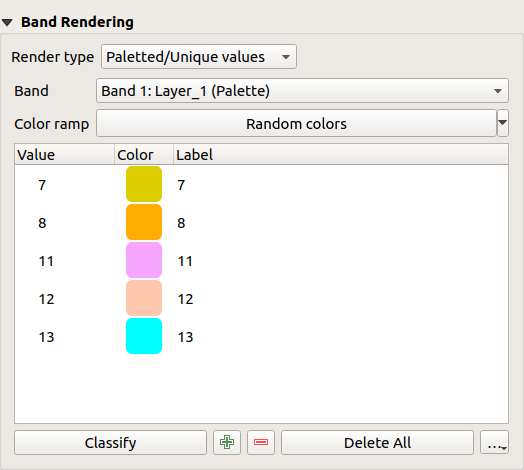
Fig. 15.3 Simbologia Raster - Visualizzazione valori a tavolozza univoci¶
The pulldown menu, that opens when clicking the … (Advanced options) button below the color map to the right, offers color map loading (Load Color Map from File…) and exporting (Export Color Map to File…), and loading of classes (Load Classes from Layer).
15.1.3.1.3. Banda singola grigia¶
This renderer allows you to render a single band layer with a Color gradient: “Black to white” or “White to black”. You can change the range of values to color (Min and Max) in the Min/Max Value Settings.
A Contrast enhancement method can be applied to the values: “No enhancement”, “Stretch to MinMax”, “Stretch and clip to MinMax” and “Clip to min max”.
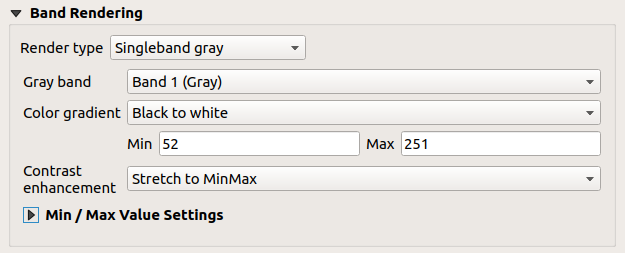
Fig. 15.4 Simbologia Raster - Visualizzazione banda singola grigia¶
15.1.3.1.4. Banda singola falso colore¶
This is a render option for single-band files that include a continuous palette. You can also create color maps for a bands of a multiband raster.
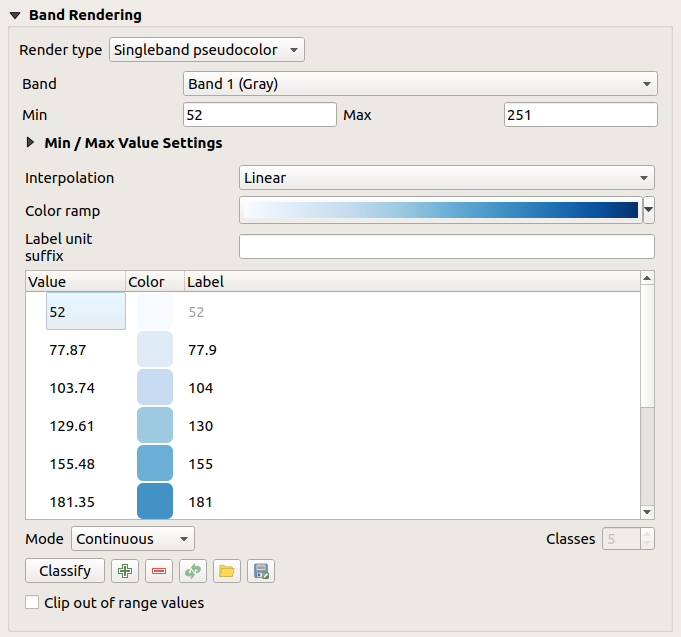
Fig. 15.5 Simbologia Raster - Visualizzazione banda singola falso colore¶
Usando una Banda singola falso colore per il layer e un values range, sono disponibili tre tipi di Interpolazione del colore:
Discrete (a
<=symbol appears in the header of the Value column)Lineare
Exact (an
=symbol appears in the header of the Value column)
The Color ramp drop down lists the available color ramps. You can create a new one and edit or save the currently selected one. The name of the color ramp will be saved in the configuration and in the QML file.
La Unità etichetta suffisso è un’etichetta aggiunta dopo il valore nella legenda.
For classification Mode  “Equal interval”,
you only need to select the number of classes
“Equal interval”,
you only need to select the number of classes
 and press the button Classify.
For Mode
and press the button Classify.
For Mode  “Continuous”, QGIS creates
classes automatically depending on Min and
Max.
“Continuous”, QGIS creates
classes automatically depending on Min and
Max.
The button  Add values manually adds a value
to the table.
The button
Add values manually adds a value
to the table.
The button  Remove selected row deletes a value from
the table.
Double clicking in the Value column lets you insert a
specific value.
Double clicking in the Color column opens the dialog
Change color, where you can select a color to apply for
that value.
Further, you can also add labels for each color, but this value won’t
be displayed when you use the identify feature tool.
Remove selected row deletes a value from
the table.
Double clicking in the Value column lets you insert a
specific value.
Double clicking in the Color column opens the dialog
Change color, where you can select a color to apply for
that value.
Further, you can also add labels for each color, but this value won’t
be displayed when you use the identify feature tool.
Right-clicking over selected rows in the color table shows a contextual menu to:
Change Color… for the selection
Change Opacity… for the selection
You can use the buttons  Load color map from file
or
Load color map from file
or  Export color map to file to load an existing
color table or to save the color table for later use.
Export color map to file to load an existing
color table or to save the color table for later use.
La  Ritaglia valori dell’intervallo permette a QGIS di non visualizzare il pixel maggiore del valore Max.
Ritaglia valori dell’intervallo permette a QGIS di non visualizzare il pixel maggiore del valore Max.
15.1.3.1.5. Ombreggiatura¶
Visualizzare una banda di un layer Raster usando l’ombreggiatura
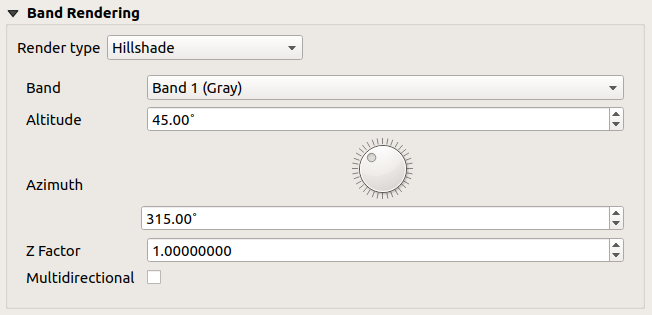
Fig. 15.6 Simbologia Raster - Visualizzazione ombreggiatura¶
Opzioni:
Banda: La banda del raster da usare.
Altitudine: L’angolo di elevazione della sorgente luminosa (il valore predefinito è
45°).Azimuth: L’azimut della sorgente luminosa (il valore predefinito è
315°).Fattore Z: Fattore di scala per i valori della banda raster (il valore predefinito è
1). Multidirezionale: Specifica se deve essere usata l’ombreggiatura multidirezionale (il valore predefinito è
Multidirezionale: Specifica se deve essere usata l’ombreggiatura multidirezionale (il valore predefinito è off`).
15.1.3.1.6. Impostazione dei valori min e max¶
By default, QGIS reports the Min and Max values of the band(s) of the raster. A few very low and/or high values can have a negative impact on the rendering of the raster. The Min/Max Value Settings frame helps you control the rendering.
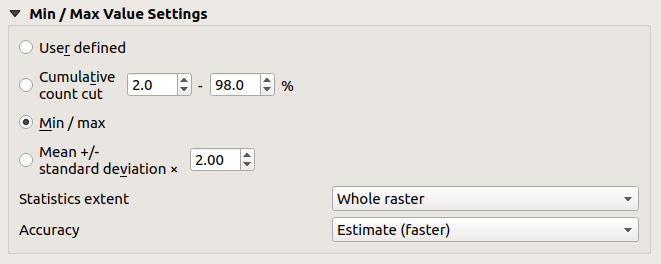
Fig. 15.7 Simbologia Raster - Impostazione dei valori Min e Max¶
Sono disponibili le opzioni:
 Definito dall’utente: I valori predefiniti Min e Max della(e) banda(i) possono essere sovrascritti.
Definito dall’utente: I valori predefiniti Min e Max della(e) banda(i) possono essere sovrascritti. Cumulative count cut: Removes outliers.
The standard range of values is
Cumulative count cut: Removes outliers.
The standard range of values is 2%to98%, but it can be adapted manually. Min / max: Uses the whole range of
values in the image band.
Min / max: Uses the whole range of
values in the image band. Mean +/- standard deviation x: Creates
a color table that only considers values within the standard
deviation or within multiple standard deviations.
This is useful when you have one or two cells with abnormally
high values in a raster layer that impact the rendering of the
raster negatively.
Mean +/- standard deviation x: Creates
a color table that only considers values within the standard
deviation or within multiple standard deviations.
This is useful when you have one or two cells with abnormally
high values in a raster layer that impact the rendering of the
raster negatively.
Il calcolo dei valori minimi e massimi delle bande viene effettuato in base a:
Statistics extent: it can be Whole raster, Current canvas or Updated canvas. Updated canvas means that min/max values used for the rendering will change with the canvas extent (dynamic stretching).
Accuracy, which can be either Estimate (faster) or Actual (slower).
Nota
Per alcune impostazioni, potrebbe essere necessario premere il pulsante Applica della finestra di dialogo delle proprietà del layer per visualizzare i valori minimi e massimi effettivi nei widget.
15.1.3.2. Visualizzazione colore¶
For all kinds of Band rendering, the Color rendering set.
You can achieve special rendering effects for your raster file(s) by using one of the blending modes (see Metodi di fusione).
Further settings can be made by modifying the Brightness, Saturation and Contrast. You can also use a Grayscale option, where you can choose between “Off”, “By lightness”, “By luminosity” and “By average”. For one Hue in the color table, you can modify the “Strength”.
15.1.3.3. Ricampionamento¶
The Resampling option has effect when you zoom in and out of an image. Resampling modes can optimize the appearance of the map. They calculate a new gray value matrix through a geometric transformation.
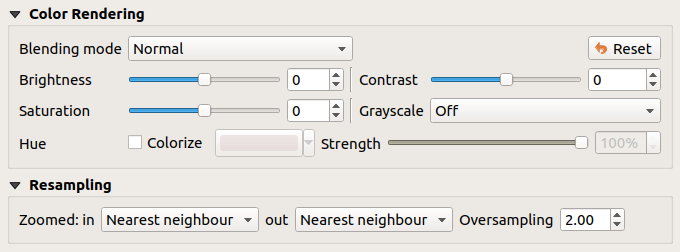
Fig. 15.8 Simbologia Raster - Visualizzazione del colore e impostazioni del Ricampionamento¶
When applying the “Nearest neighbour” method, the map can get a pixelated structure when zooming in. This appearance can be improved by using the “Bilinear” or “Cubic” method, which cause sharp edges to be blurred. The effect is a smoother image. This method can be applied to for instance digital topographic raster maps.
Nella parte inferiore della scheda Simbologia, puoi vedere una miniatura del layer, della legenda e della tavolozza.
15.1.4. Proprietà Trasparenza¶
 QGIS has the ability to set the transparency level
of a raster layer.
Use the transparency slider
QGIS has the ability to set the transparency level
of a raster layer.
Use the transparency slider  to set to what extent the
underlying layers (if any) should be visible through the current
raster layer.
This is very useful if you overlay raster layers (e.g., a shaded
relief map overlayed by a classified raster map).
This will make the look of the map more three dimensional.
to set to what extent the
underlying layers (if any) should be visible through the current
raster layer.
This is very useful if you overlay raster layers (e.g., a shaded
relief map overlayed by a classified raster map).
This will make the look of the map more three dimensional.
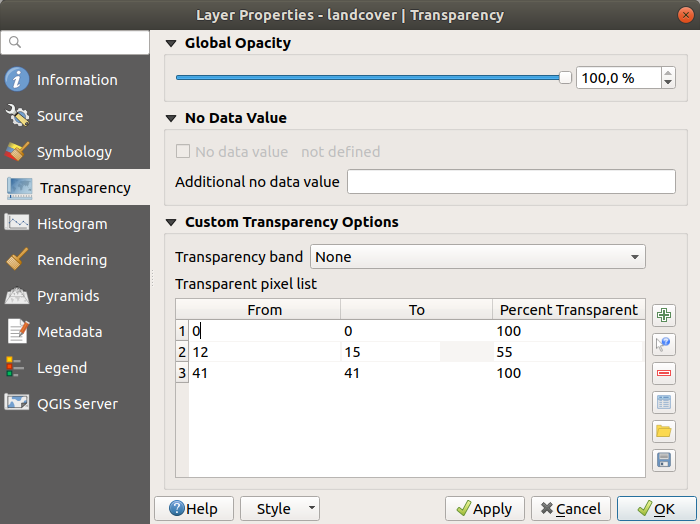
Fig. 15.9 Trasparenza Raster¶
Additionally, you can enter a raster value that should be treated as an Additional no data value.
An even more flexible way to customize the transparency is available in the Custom transparency options section:
Use Transparency band to apply transparency for an entire band.
Provide a list of pixels to make transparent with corresponding levels of transparency:
Clicca sul pulsante
 Aggiungi valori manualmente. Apparirà cosi una nuova riga.
Aggiungi valori manualmente. Apparirà cosi una nuova riga.Inserisci i valori Rosso, Verde e Blu del pixel e regola la Percentuale Trasparenza da applicare.
Alternatively, you can fetch the pixel values directly from the raster using the
 Add values from display
button.
Then enter the transparency value.
Add values from display
button.
Then enter the transparency value.Ripeti i passi per regolare più valori con una trasparenza personalizzata.
Premi il pulsante Applica e dai una controllata alla mappa.
Come puoi vedere è molto semplice impostare una trasparenza personalizzata, però richiede comunque un po’ di lavoro. Proprio per questo puoi usare il pulsante
 Esporta su file per salvare la lista dei valori su un file esterno. Il pulsante
Esporta su file per salvare la lista dei valori su un file esterno. Il pulsante  Importa da file ti permette di caricare le impostazioni di trasparenza e applicarle al raster selezionato.
Importa da file ti permette di caricare le impostazioni di trasparenza e applicarle al raster selezionato.
15.1.5. Proprietà Istogramma¶
The  Histogram tab allows you to view
the distribution of the values in your raster.
The histogram is generated when you press the
Compute Histogram button.
All existing bands will be displayed together.
You can save the histogram as an image with the
Histogram tab allows you to view
the distribution of the values in your raster.
The histogram is generated when you press the
Compute Histogram button.
All existing bands will be displayed together.
You can save the histogram as an image with the  button.
button.
Nella parte inferiore dell’istogramma, puoi selezionare una banda raster nel menu a discesa e Imposta stile min/max per. Il menu a discesa  Preferiti/Azioni offre opzioni avanzate per personalizzare l’istogramma:
Preferiti/Azioni offre opzioni avanzate per personalizzare l’istogramma:
With the Visibility option, you can display histograms for individual bands. You will need to select the option
 Show selected band.
Show selected band.Le Opzioni Min/max permettono di “Mostra sempre i simboli min/max”, “Zoom a min/max” e “Aggiorna stile a min/max”.
The Actions option allows you to “Reset” or “Recompute histogram” after you have changed the min or max values of the band(s).
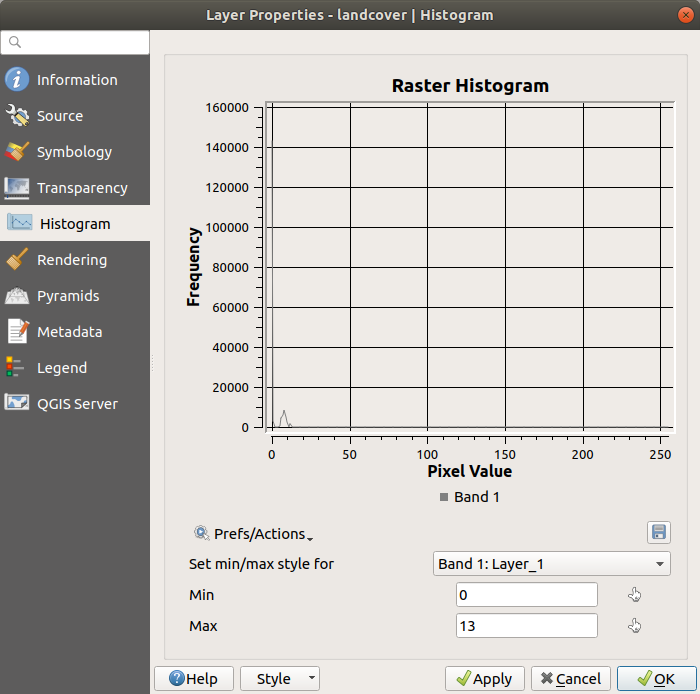
Fig. 15.10 Istogramma del raster¶
15.1.6. Proprietà Visualizzazione¶
Nella scheda 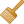 Visualizzazione, è possibile:
Visualizzazione, è possibile:
set Scale dependent visibility for the layer: You can set the Maximum (inclusive) and Minimum (exclusive) scale, defining a range of scales in which the layer will be visible. It will be hidden outside this range. The
 Set to current canvas scale button
helps you use the current map canvas scale as a boundary.
See Visualizzazione in funzione della scala for more information.
Set to current canvas scale button
helps you use the current map canvas scale as a boundary.
See Visualizzazione in funzione della scala for more information.Refresh layer at interval (seconds): set a timer to automatically refresh individual layers. Canvas updates are deferred in order to avoid refreshing multiple times if more than one layer has an auto update interval set.
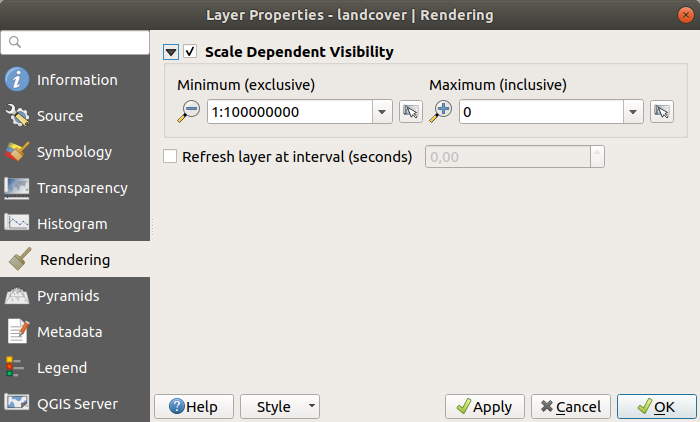
Fig. 15.11 Visualizzazione Raster¶
15.1.7. Proprietà Piramidi¶
High resolution raster layers can slow navigation in QGIS. By creating lower resolution copies of the data (pyramids), performance can be considerably improved, as QGIS selects the most suitable resolution to use depending on the zoom level.
Per creare piramidi devi avere i permessi di scrittura nella cartella contenente il dato originale: in questa cartella verranno salvate le copie a bassa risoluzione.
From the Resolutions list, select resolutions at which you want to create pyramid levels by clicking on them.
Se scegli Interno (se possibile) dal menu a tendina Formato panoramica, QGIS proverà a costruire le piramidi internamente.
Nota
Please note that building pyramids may alter the original data file, and once created they cannot be removed. If you wish to preserve a “non-pyramided” version of your raster, make a backup copy prior to pyramid building.
Se scegli Esterno e Esterno (immagine Erdas) le piramidi verranno create in un file accanto al raster originale con lo stesso nome e un’estensione .ovr.
Several Resampling methods can be used for pyramid calculation:
Vicino più prossimo (metodo Nearest Neighbour)
Media
Gauss
Cubico
Spline Cubica
Laczos
Moda
Nessuno
Infine, fai clic su Costruisci piramidi per avviare il processo.
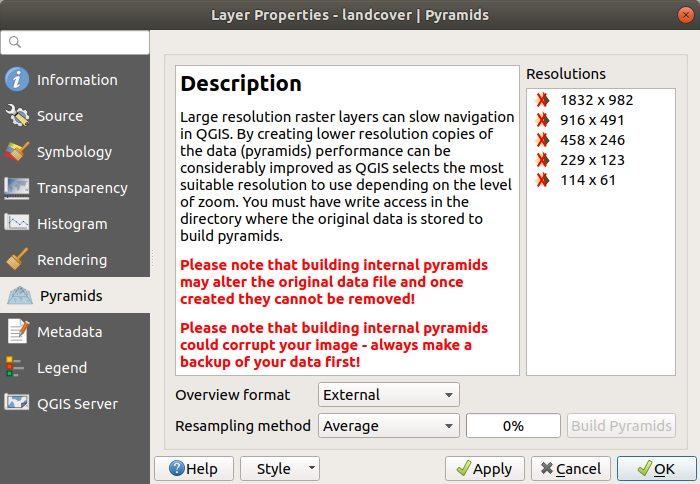
Fig. 15.12 Piramidi raster¶
15.1.8. Proprietà Metadati¶
La scheda  Metadati ti fornisce le opzioni per creare e modificare un report dei metadati sul tuo layer. Vedi vector layer metadata properties per ulteriori informazioni.
Metadati ti fornisce le opzioni per creare e modificare un report dei metadati sul tuo layer. Vedi vector layer metadata properties per ulteriori informazioni.
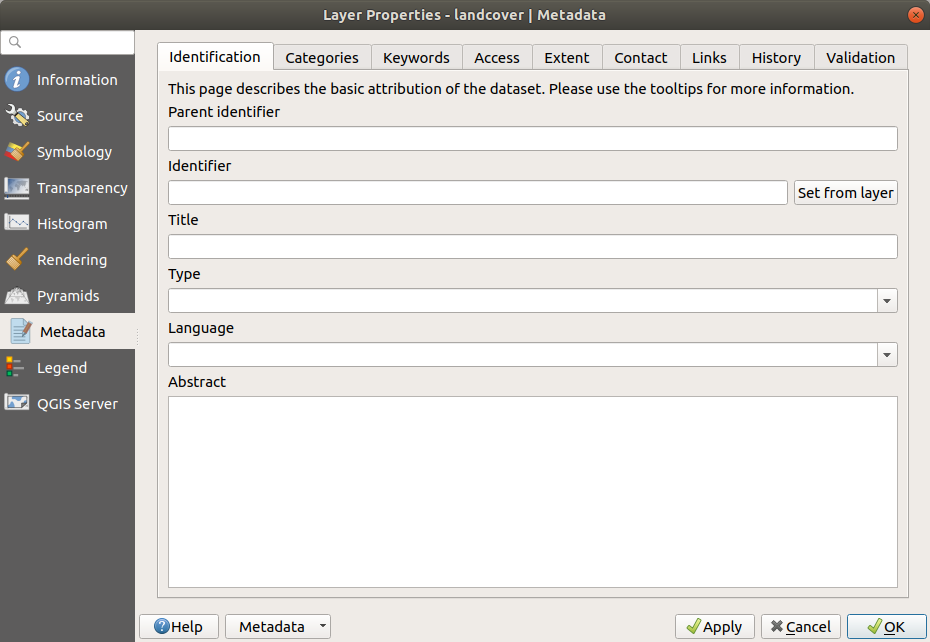
Fig. 15.13 Raster Metadata¶
15.1.9. Proprietà Legenda¶
La scheda  Legenda ti fornisce una lista di widget che puoi inserire all’interno dell’albero dei layer nel Pannello Layer. L’idea è quella di avere un modo per accedere rapidamente ad alcune azioni che sono spesso usate con il layer (impostazioni trasparenza, filtraggio, selezione, stile o altre cose….).
Legenda ti fornisce una lista di widget che puoi inserire all’interno dell’albero dei layer nel Pannello Layer. L’idea è quella di avere un modo per accedere rapidamente ad alcune azioni che sono spesso usate con il layer (impostazioni trasparenza, filtraggio, selezione, stile o altre cose….).
By default, QGIS provides a transparency widget but this can be extended by plugins that register their own widgets and assign custom actions to layers they manage.
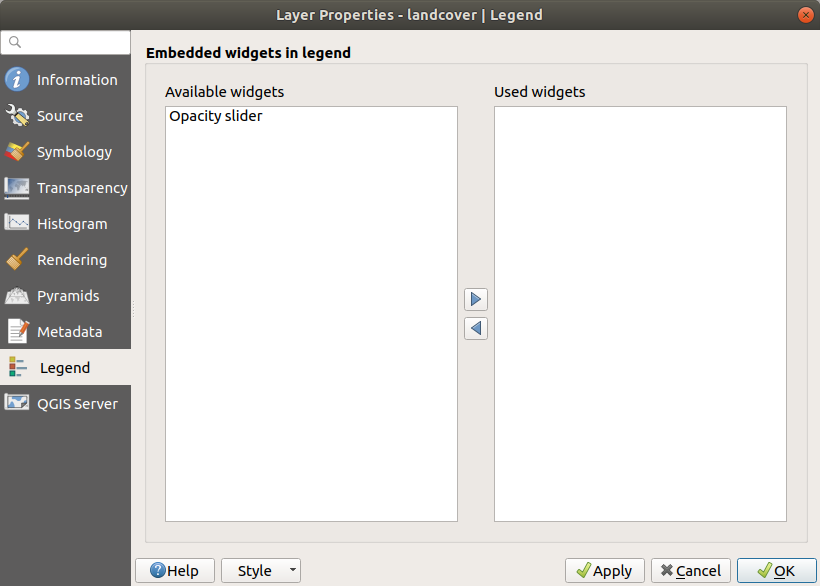
Fig. 15.14 Raster Legend¶
15.1.10. Proprietà Server QGIS¶
From the  QGIS Server tab, information can
be provided for Description, Attribution,
MetadataUrl and LegendUrl.
QGIS Server tab, information can
be provided for Description, Attribution,
MetadataUrl and LegendUrl.
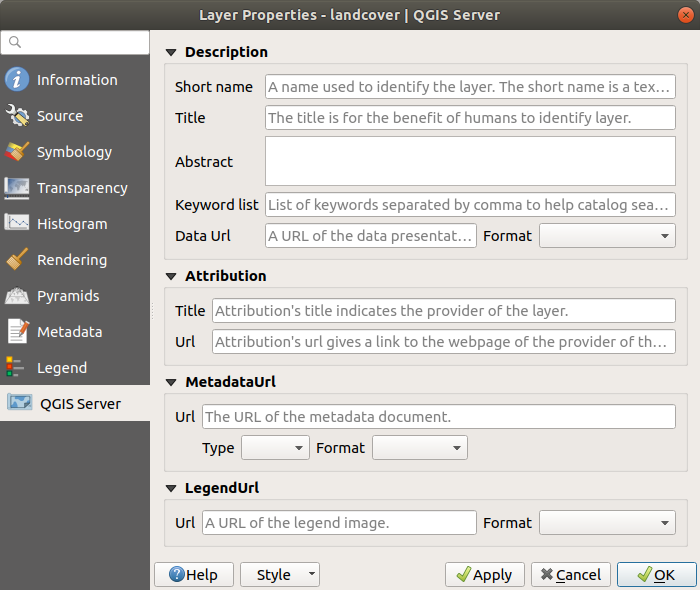
Fig. 15.15 QGIS Server nelle Proprietà Raster¶

