Indice
- User guide/Manual
- Introduzione
- Convenzioni
- Premessa
- Caratteristiche
- What’s new in QGIS 2.8
- Come Iniziare
- QGIS GUI
- Strumenti generali
- QGIS Configuration
- Lavorare con le proiezioni
- QGIS Browser
- Lavorare con i vettori
- Lavorare con i dati raster
- Lavorare con i dati OGC
- Lavorare con i dati GPS
- Integrazione con GRASS GIS
- QGIS processing framework
- Processing providers and algorithms
- Compositore di stampe
- Plugin di QGIS
- Aiuto e supporto
- Appendice
- Letteratura e riferimenti web
- User guide/Manual PDF’s
- PyQGIS cookbook
- Documentation Guidelines
- A gentle introduction in GIS
- Trainings manual
.
Proprietà raster¶
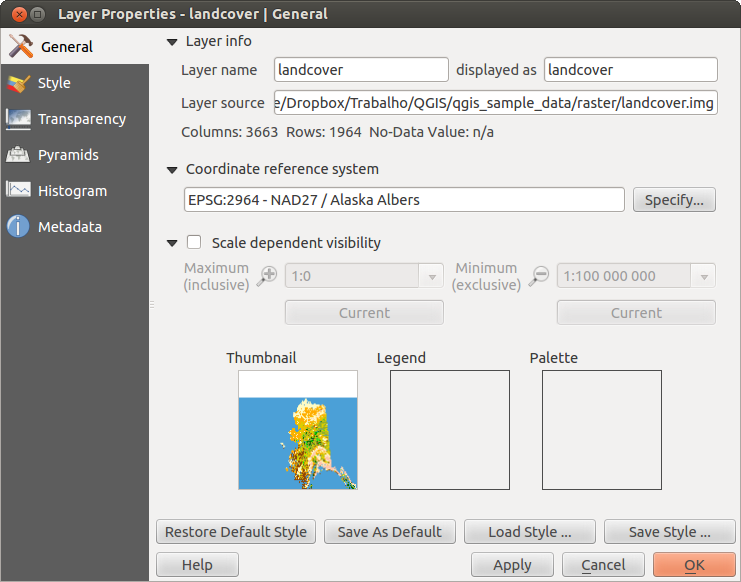
Per visualizzare ed impostare le proprietà di un raster, fai doppio click sul nome del raster nella legenda o cliccaci sopra con il tasto destro e scegli Proprietà dal menu contestuale. Si aprirà cosi la finestra di dialogo Proprietà del layer (vedi figure_raster_1).
Ci sono diversi menu nella finestra di dialogo:
Generale
Stile
Trasparenza
Piramidi
Istogramma
Metadati
Figure Raster 1:
Menu Generale¶
Informazioni del layer¶
Il menu Generale contiene informazioni basilari del raster selezionato, inclusa la sorgente del file, il nome visualizzato nella legenda (che puoi modificare) e il numero di colonne, righe e valori nulli.
Sistema Riferimento Coordinate¶
Qui puoi trovare il sistema di riferimento spaziale (SR) visualizzato in formato stringa PROJ.4. Se l’impostazione non è corretta la puoi modificare con il pulsante [Specifica].
Visibilità dipendente dalla scala¶
In questo menu puoi attivare la funzione che imposta la visibilità del raster in funzione della scala. Spuntando la casella di controllo puoi impostare l’intervallo di scala in cui vuoi che il raster venga visualizzato nella mappa.
Nella parte inferiore puoi vedere un’anteprima del raster, la sua simbologia e la tavolozza.
Menu Stile¶
Visualizzazione banda¶
QGIS offers four different Render types. The renderer chosen is dependent on the data type.
Colori banda multipla - se il file è caricato come multibanda e ha diverse bande di colori (per esempio un’immagine satellitare con molte bande diverse)
Tavolozza - se un file ha una tavolozza indicizzata (per esempio una mappa topografica digitale)
- Singleband gray - (one band of) the image will be rendered as gray; QGIS will choose this renderer if the file has neither multibands nor an indexed palette nor a continous palette (e.g., used with a shaded relief map)
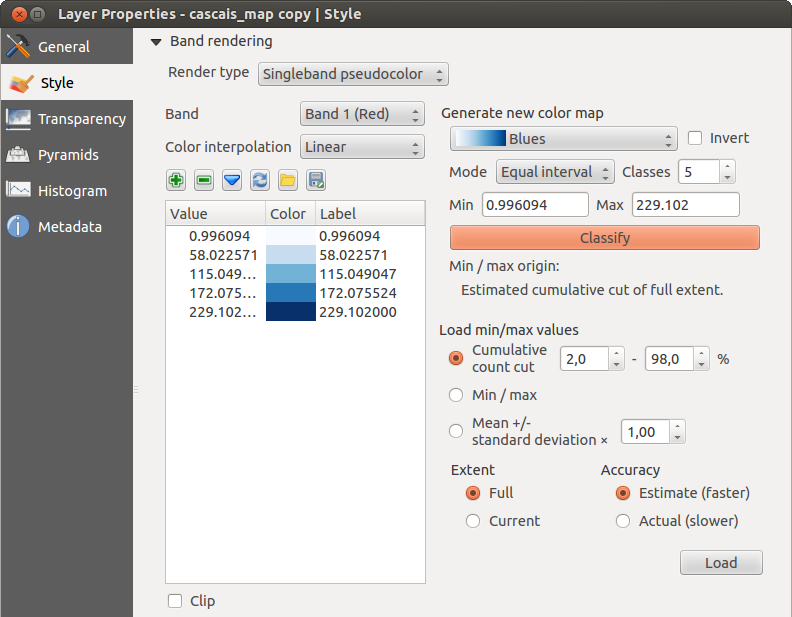
Banda singola falso colore - puoi usare questo visualizzatore per i file che hanno una tavolozza continua o una mappa di colore (per esempio una mappa delle altimetrie)
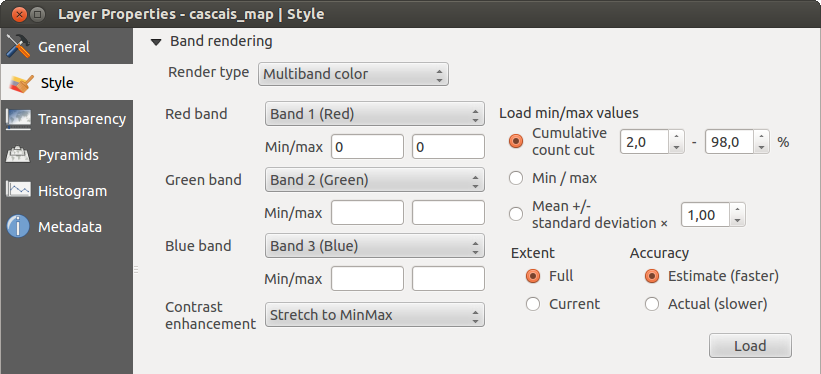
Colori banda multipla
Con il visualizzatore colore banda multipla verranno visualizzate le tre bande selezionate dell’immagine, ognuna delle quali corrisponde alle componenti rosso, verde e blu che verranno usate per creare i colori dell’immagine stessa. Puoi scegliere fra diversi metodi di Miglioramento contrasto: ‘Nessun miglioramento’, ‘Stira a MinMax’, ‘Stira e taglia a MinMax’ e ‘Taglia a MinMax’.
Figure Raster 2:
This selection offers you a wide range of options to modify the appearance
of your raster layer. First of all, you have to get the data range from your
image. This can be done by choosing the Extent and pressing
[Load]. QGIS can  Estimate (faster) the
Min and Max values of the bands or use the
Estimate (faster) the
Min and Max values of the bands or use the
 Actual (slower) Accuracy.
Actual (slower) Accuracy.
Now you can scale the colors with the help of the Load min/max values section.
A lot of images have a few very low and high data. These outliers can be eliminated
using the  Cumulative count cut setting. The standard data range is set
from 2% to 98% of the data values and can be adapted manually. With this
setting, the gray character of the image can disappear.
With the scaling option
Cumulative count cut setting. The standard data range is set
from 2% to 98% of the data values and can be adapted manually. With this
setting, the gray character of the image can disappear.
With the scaling option  Min/max, QGIS creates a color table with all of
the data included in the original image (e.g., QGIS creates a color table
with 256 values, given the fact that you have 8 bit bands).
You can also calculate your color table using the
Min/max, QGIS creates a color table with all of
the data included in the original image (e.g., QGIS creates a color table
with 256 values, given the fact that you have 8 bit bands).
You can also calculate your color table using the  Mean +/- standard deviation x
Mean +/- standard deviation x  .
Then, only the values within the standard deviation or within multiple standard deviations
are considered for the color table. This is useful when you have one or two cells
with abnormally high values in a raster grid that are having a negative impact on
the rendering of the raster.
.
Then, only the values within the standard deviation or within multiple standard deviations
are considered for the color table. This is useful when you have one or two cells
with abnormally high values in a raster grid that are having a negative impact on
the rendering of the raster.
All calculations can also be made for the  Current extent.
Current extent.
Suggerimento
Visualizzare una singola banda di un raster multibanda
Se vuoi vedere solamente una banda singola di un’immagine multibanda (per esempio, rossa) potresti pensare di impostare le bande verde e blu come “Non impostato”. Ma questo non è il miglior modo di agire. Per visualizzare la banda rossa, seleziona il visualizzatore ‘Banda grigia singola’ e poi seleziona il rosso come colore da usare al posto del grigio.
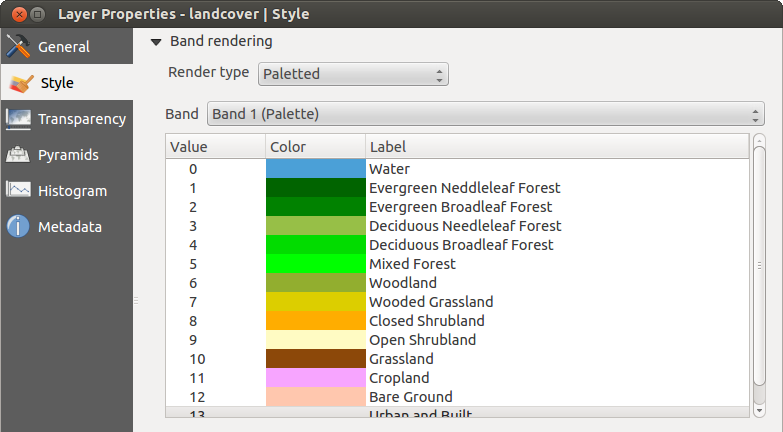
Tavolozza
This is the standard render option for singleband files that already include a color table, where each pixel value is assigned to a certain color. In that case, the palette is rendered automatically. If you want to change colors assigned to certain values, just double-click on the color and the Select color dialog appears. Also, in QGIS 2.2. it’s now possible to assign a label to the color values. The label appears in the legend of the raster layer then.
Figure Raster 3:
Miglioramento contrasto
Nota
When adding GRASS rasters, the option Contrast enhancement will always be set automatically to stretch to min max, regardless of if this is set to another value in the QGIS general options.
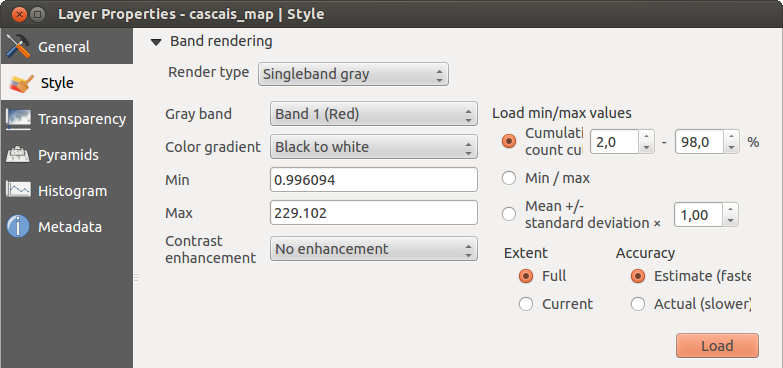
Banda singola grigia
This renderer allows you to render a single band layer with a Color gradient:
‘Black to white’ or ‘White to black’. You can define a Min
and a Max value by choosing the Extent first and
then pressing [Load]. QGIS can  Estimate (faster) the
Min and Max values of the bands or use the
Estimate (faster) the
Min and Max values of the bands or use the
 Actual (slower) Accuracy.
Actual (slower) Accuracy.
Figure Raster 4:
With the Load min/max values section, scaling of the color table
is possible. Outliers can be eliminated using the  Cumulative count cut setting.
The standard data range is set from 2% to 98% of the data values and can
be adapted manually. With this setting, the gray character of the image can disappear.
Further settings can be made with
Cumulative count cut setting.
The standard data range is set from 2% to 98% of the data values and can
be adapted manually. With this setting, the gray character of the image can disappear.
Further settings can be made with  Min/max and
Min/max and
 Mean +/- standard deviation x
Mean +/- standard deviation x  .
While the first one creates a color table with all of the data included in the
original image, the second creates a color table that only considers values
within the standard deviation or within multiple standard deviations.
This is useful when you have one or two cells with abnormally high values in
a raster grid that are having a negative impact on the rendering of the raster.
.
While the first one creates a color table with all of the data included in the
original image, the second creates a color table that only considers values
within the standard deviation or within multiple standard deviations.
This is useful when you have one or two cells with abnormally high values in
a raster grid that are having a negative impact on the rendering of the raster.
Banda singola falso colore
This is a render option for single-band files, including a continous palette. You can also create individual color maps for the single bands here.
Figure Raster 5:
Sono disponibili tre tipologie di interpolazione di colore:
Discreto
Lineare
Esatto
In the left block, the button  Add values manually adds a value to the
individual color table. The button
Add values manually adds a value to the
individual color table. The button 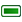 Remove selected row
deletes a value from the individual color table, and the
Remove selected row
deletes a value from the individual color table, and the
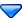 Sort colormap items button sorts the color table according
to the pixel values in the value column. Double clicking on the value column lets
you insert a specific value. Double clicking on the color column opens the dialog
Change color, where you can select a color to apply on that value. Further,
you can also add labels for each color, but this value won’t be displayed when you use the identify
feature tool.
You can also click on the button
Sort colormap items button sorts the color table according
to the pixel values in the value column. Double clicking on the value column lets
you insert a specific value. Double clicking on the color column opens the dialog
Change color, where you can select a color to apply on that value. Further,
you can also add labels for each color, but this value won’t be displayed when you use the identify
feature tool.
You can also click on the button  Load color map from band,
which tries to load the table from the band (if it has any). And you can use the
buttons
Load color map from band,
which tries to load the table from the band (if it has any). And you can use the
buttons  Load color map from file or
Load color map from file or  Export color map to file to load an existing color table or to save the
defined color table for other sessions.
Export color map to file to load an existing color table or to save the
defined color table for other sessions.
In the right block, Generate new color map allows you to create newly
categorized color maps. For the Classification mode 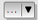 ‘Equal interval’,
you only need to select the number of classes
‘Equal interval’,
you only need to select the number of classes
 and press the button Classify. You can invert the colors
of the color map by clicking the
and press the button Classify. You can invert the colors
of the color map by clicking the  Invert
checkbox. In the case of the Mode
Invert
checkbox. In the case of the Mode  ‘Continous’, QGIS creates
classes automatically depending on the Min and Max.
Defining Min/Max values can be done with the help of the Load min/max values section.
A lot of images have a few very low and high data. These outliers can be eliminated
using the
‘Continous’, QGIS creates
classes automatically depending on the Min and Max.
Defining Min/Max values can be done with the help of the Load min/max values section.
A lot of images have a few very low and high data. These outliers can be eliminated
using the  Cumulative count cut setting. The standard data range is set
from 2% to 98% of the data values and can be adapted manually. With this
setting, the gray character of the image can disappear.
With the scaling option
Cumulative count cut setting. The standard data range is set
from 2% to 98% of the data values and can be adapted manually. With this
setting, the gray character of the image can disappear.
With the scaling option  Min/max, QGIS creates a color table with all of
the data included in the original image (e.g., QGIS creates a color table
with 256 values, given the fact that you have 8 bit bands).
You can also calculate your color table using the
Min/max, QGIS creates a color table with all of
the data included in the original image (e.g., QGIS creates a color table
with 256 values, given the fact that you have 8 bit bands).
You can also calculate your color table using the  Mean +/- standard deviation x
Mean +/- standard deviation x  .
Then, only the values within the standard deviation or within multiple standard deviations
are considered for the color table.
.
Then, only the values within the standard deviation or within multiple standard deviations
are considered for the color table.
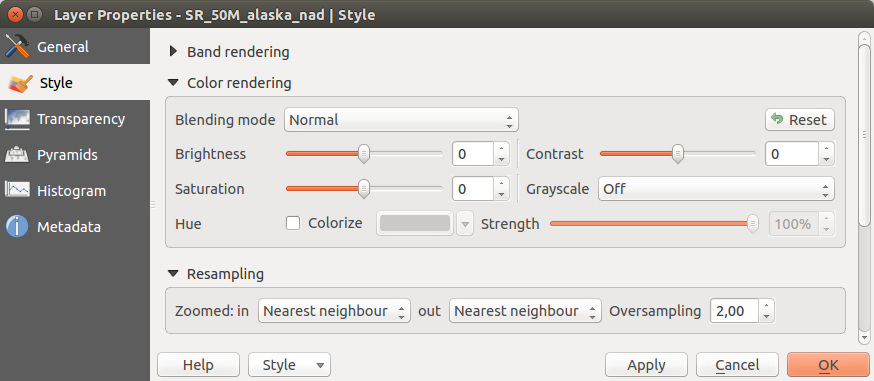
Visualizzazione colore¶
Per ogni Visualizzazione banda, è disponibile una Visualizzazione colore.
Puoi anche ottenere effetti speciali per i tuoi raster usando una delle modalità fusione (vedi Proprietà dei vettori).
Further settings can be made in modifiying the Brightness, the Saturation and the Contrast. You can also use a Grayscale option, where you can choose between ‘By lightness’, ‘By luminosity’ and ‘By average’. For one hue in the color table, you can modify the ‘Strength’.
Ricampionamento¶
La sezione Ricampionamento ha effetto quando ingrandisci o rimpicciolisci l’immagine. I metodi di ricampionamento ottimizzano l’aspetto della mappa perché calcolano una nuova matrice di grigi attraverso una trasformazione geometrica.
Figure Raster 6:
Applicando il metodo ‘vicino più prossimo’ la mappa potrebbe avere una struttura con molti pixel quando viene ingrandita. Questo aspetto può essere migliorato usando i metodi ‘Bilineare’ o ‘Cubico’ perché creano delle geometrie più appuntite e offuscate. Il risultato è un’immagine più morbida. Puoi applicare questo metodo, per esempio, a mappe raster topografiche.
Menu Trasparenza¶
QGIS has the ability to display each raster layer at a different transparency level.
Use the transparency slider  to indicate to what extent the underlying layers
(if any) should be visible though the current raster layer. This is very useful
if you like to overlay more than one raster layer (e.g., a shaded relief map
overlayed by a classified raster map). This will make the look of the map more
three dimensional.
to indicate to what extent the underlying layers
(if any) should be visible though the current raster layer. This is very useful
if you like to overlay more than one raster layer (e.g., a shaded relief map
overlayed by a classified raster map). This will make the look of the map more
three dimensional.
Inoltre puoi inserire nel menu Valori nulli aggiuntivi un valore che deve essere trattato come Valore nullo.
Puoi definire la trasparenza in maniera ancora più dettagliata e personalizzata nella sezione Opzioni di trasparenza personalizzate, nella quale puoi impostare il grado di trasparenza di ogni singola cella (o pixel).
As an example, we want to set the water of our example raster file landcover.tif to a transparency of 20%. The following steps are neccessary:
Carica il file
Apri la finestra di dialogo Proprietà facendo doppio click sul nome del raster nella legenda o cliccando su di esso con il tasto destro del mouse e scegliendo Proprietà dal menu contestuale.
Seleziona il menu Trasparenza.
Scegli ‘Nessuno’ dal menu Banda trasparenza.
- Click the
 Add values manually
button. A new row will appear in the pixel list.
Add values manually
button. A new row will appear in the pixel list. Inserisci il valore nelle colonne ‘Da’ e ‘A’ (nell’esempio viene usato 0) e aggiusta la trasparenza al 20%.
Clicca sul pulsante [Applica] per visualizzare il risultato.
Ripeti i passaggi 5 e 6 per aggiustare più valori con trasparenze personalizzate.
As you can see, it is quite easy to set custom transparency, but it can be
quite a lot of work. Therefore, you can use the button  Export to file to save your transparency list to a file. The button
Export to file to save your transparency list to a file. The button
 Import from file loads your transparency settings and
applies them to the current raster layer.
Import from file loads your transparency settings and
applies them to the current raster layer.
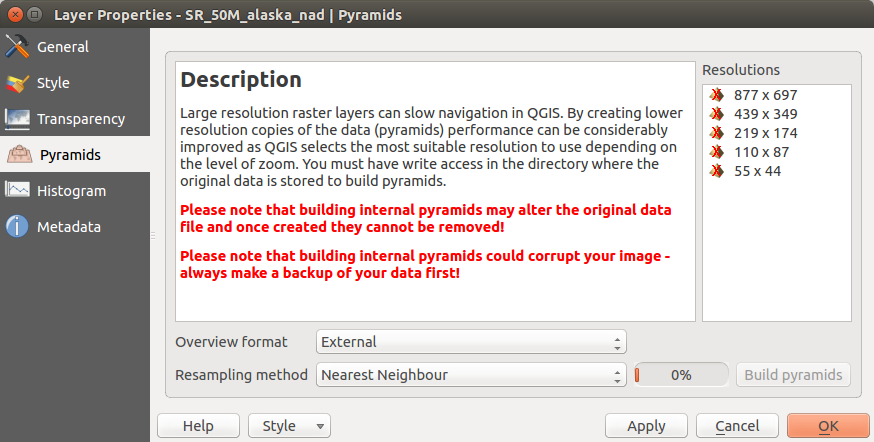
Menu Piramidi¶
Large resolution raster layers can slow navigation in QGIS. By creating lower resolution copies of the data (pyramids), performance can be considerably improved, as QGIS selects the most suitable resolution to use depending on the level of zoom.
Per creare piramidi devi avere i permessi di scrittura nella cartella contenente il dato originale: in questa cartella verranno salvate le copie a bassa risoluzione.
Sono disponibili i seguenti metodi di ricampionamento:
Vicino più prossimo (metodo Nearest Neighbour)
Media
- Gauss
Cubico
Modo
Nessuno
If you choose ‘Internal (if possible)’ from the Overview format menu, QGIS tries to build pyramids internally. You can also choose ‘External’ and ‘External (Erdas Imagine)’.
Figure Raster 7:
La costruzione delle piramidi può alterare il dato originale in maniera irreversibile, quindi ti raccomandiamo di fare una copia del raster originale prima di eseguire l’operazione.
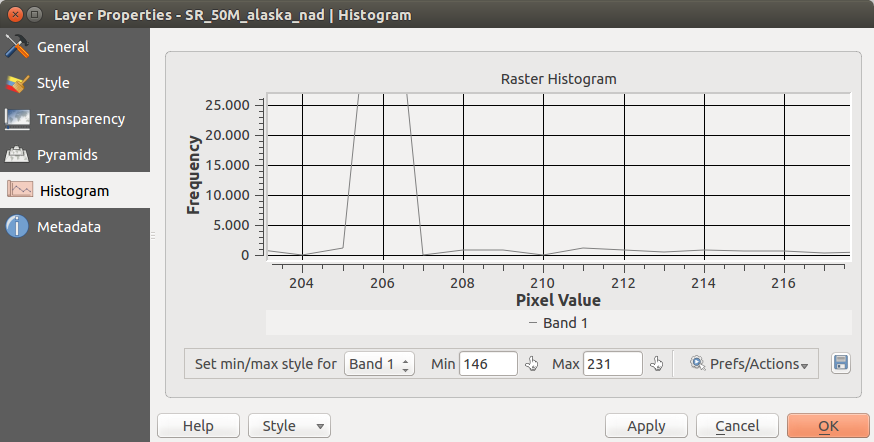
Menu Istogramma¶
The Histogram menu allows you to view the distribution of the bands
or colors in your raster. The histogram is generated automatically when you open the
Histogram menu. All existing bands will be displayed together. You can
save the histogram as an image with the  button.
With the Visibility option in the
button.
With the Visibility option in the  Prefs/Actions menu,
you can display histograms of the individual bands. You will need to select the option
Prefs/Actions menu,
you can display histograms of the individual bands. You will need to select the option
 Show selected band.
The Min/max options allow you to ‘Always show min/max markers’, to ‘Zoom
to min/max’ and to ‘Update style to min/max’.
With the Actions option, you can ‘Reset’ and ‘Recompute histogram’ after
you have chosen the Min/max options.
Show selected band.
The Min/max options allow you to ‘Always show min/max markers’, to ‘Zoom
to min/max’ and to ‘Update style to min/max’.
With the Actions option, you can ‘Reset’ and ‘Recompute histogram’ after
you have chosen the Min/max options.
Figure Raster 8:
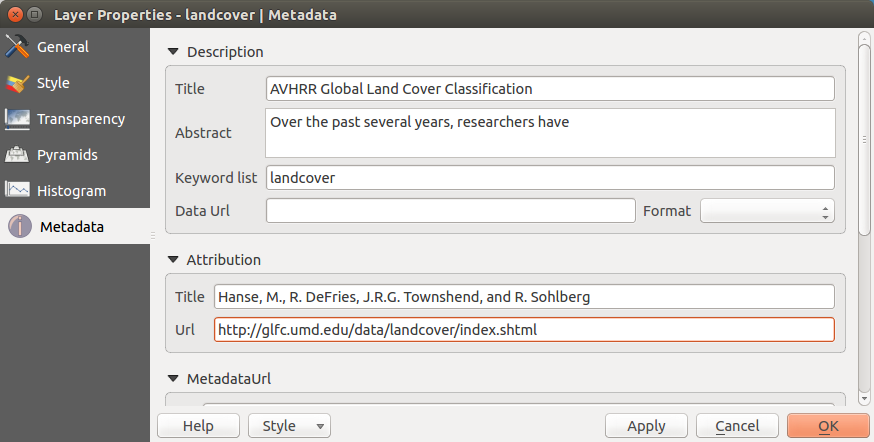
Menu Metadati¶
La scheda Metadati mostra una serie di informazioni sul raster, incluse le statistiche di ogni banda. Da questo menu hai accesso a diverse sezioni: Descrizione, Assegnazione, URL Metadati e Proprietà. Nella sezione Proprietà le statistiche sono ottenute da una base ‘che si deve ancora conoscere’, quindi è meglio che le statistiche di questo raster non siano ancora state calcolate.
Figure Raster 9: