.
QGIS as OGC Data Client¶
El Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) es una organización internacional con miembros de más de 300 organizaciones comerciales, gubernamentales, sin fines de lucro y de investigación de todo el mundo. Sus miembros desarrollan e implementan estándares para contenido geoespacial y servicios, procesamiento de datos SIG y el intercambio.
Al describir un modelo de datos básico para las características geográficas, un número cada vez mayor de las especificaciones son desarrollados por OGC para atender las necesidades específicas de ubicación interoperable y la tecnología geoespacial, incluyendo SIG. Más información se puede encontrar en http://www.opengeospatial.org/.
Important OGC specifications supported by QGIS are:
- WMS — Web Map Service (Cliente WMS/WMTS)
- WMTS — Web Map Tile Service (Cliente WMS/WMTS)
- WFS — Web Feature Service (Cliente WFS y WFS-T)
- WFS-T — Web Feature Service - Transactional (Cliente WFS y WFS-T)
- WCS — Web Coverage Service (WCT Cliente)
- SFS — Simple Features for SQL (Capas PostGIS)
GML — Lenguaje de Marcado Generalizado
OGC services are increasingly being used to exchange geospatial data between different GIS implementations and data stores. QGIS can deal with the above specifications as a client, being SFS (through support of the PostgreSQL / PostGIS data provider, see section Capas PostGIS).
Cliente WMS/WMTS¶
Información general de la implementación WMS¶
QGIS currently can act as a WMS client that understands WMS 1.1, 1.1.1 and 1.3 servers. In particular, it has been tested against publicly accessible servers such as DEMIS.
A WMS server acts upon requests by the client (e.g., QGIS) for a raster map with a given extent, set of layers, symbolization style, and transparency. The WMS server then consults its local data sources, rasterizes the map, and sends it back to the client in a raster format. For QGIS, this format would typically be JPEG or PNG.
WMS is generically a REST (Representational State Transfer) service rather than a full-blown Web service. As such, you can actually take the URLs generated by QGIS and use them in a web browser to retrieve the same images that QGIS uses internally. This can be useful for troubleshooting, as there are several brands of WMS server on the market and they all have their own interpretation of the WMS standard.
Las capas WMS se pueden añadir sencillamente, siempre que conozca la URL para acceder al servidor WMS, si tiene una conexión útil a ese servidor, y el servidor entiende HTTP como mecanismo de transporte de datos.
Información general de la implementación WMTS¶
QGIS can also act as a WMTS client. WMTS is an OGC standard for distributing tile sets of geospatial data. This is a faster and more efficient way of distributing data than WMS because with WMTS, the tile sets are pre-generated, and the client only requests the transmission of the tiles, not their production. A WMS request typically involves both the generation and transmission of the data. A well-known example of a non-OGC standard for viewing tiled geospatial data is Google Maps.
Para mostrar los datos en una variedad de escalas cercanas a lo que el usuario podría querer, los conjuntos de teselas WMTS se producen en varios niveles de escala diferentes y están disponibles para el cliente SIG para pedirlos.
Este diagrama ejemplifica el concepto de conjunto de teselas:
Figure WMTS 1:
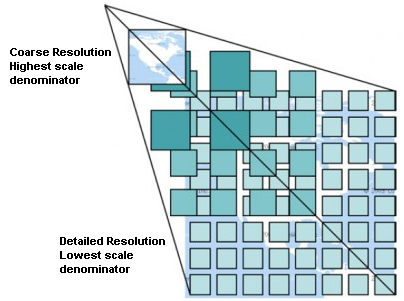
Concepto de conjunto de teselas WMTS
The two types of WMTS interfaces that QGIS supports are via Key-Value-Pairs (KVP) and RESTful. These two interfaces are different, and you need to specify them to QGIS differently.
1) In order to access a WMTS KVP service, a QGIS user must open the WMS/WMTS interface and add the following string to the URL of the WMTS tile service:
"?SERVICE=WMTS&REQUEST=GetCapabilities"
Un ejemplo de este tipo de dirección es
http://opencache.statkart.no/gatekeeper/gk/gk.open_wmts?\
service=WMTS&request=GetCapabilities
Para probar la capa topo2 en este WMTS funciona muy bien. Añadir esta cadena indica que un servicio web WMTS se va a utilizar en lugar de un servicio WMS.
EL servicio RESTful WMTS toma una forma diferente, una URL sencilla. EL formato recomendado por OGC es:
{WMTSBaseURL}/1.0.0/WMTSCapabilities.xml
This format helps you to recognize that it is a RESTful address. A RESTful WMTS is accessed in QGIS by simply adding its address in the WMS setup in the URL field of the form. An example of this type of address for the case of an Austrian basemap is http://maps.wien.gv.at/basemap/1.0.0/WMTSCapabilities.xml.
Nota
You can still find some old services called WMS-C. These services are quite similar to WMTS (i.e., same purpose but working a little bit differently). You can manage them the same as you do WMTS services. Just add ?tiled=true at the end of the url. See http://wiki.osgeo.org/wiki/Tile_Map_Service_Specification for more information about this specification.
Cuando se lee WMTS, a menudo se puede pensar en WMS-C también.
Seleccionar servidor WMS/WMTS¶
The first time you use the WMS feature in QGIS, there are no servers defined.
Begin by clicking the  Add WMS layer button on the
toolbar, or selecting Layer ‣ Add WMS Layer....
Add WMS layer button on the
toolbar, or selecting Layer ‣ Add WMS Layer....
El diálogo Añadir capa(s) desde un servidor para añadir capas que aparezcan en el servidor WMS. Se pueden agregar algunas capas para jugar haciendo clic en el botón [Añadir servidores predeterminados]. Este añadirá dos servidores demo WMS para usar: los servidores WMS de DM Solutions Group y Lizardtech. Para definir un nuevo servidor WMS en la pestaña Capas, seleccionar el botón [Nuevo]. A continuación introduzca los parámetros para conectarse a su servidor deseado, como se indica en table_OGC_1:
Tabla OGC 1: Parámetros de conexión WMS
If you need to set up a proxy server to be able to receive WMS services from the
internet, you can add your proxy server in the options. Choose
Settings ‣ Options and click on the Network & Proxy tab.
There, you can add your proxy settings and enable them by setting  Use proxy for web access. Make sure that you select the correct
proxy type from the Proxy type
Use proxy for web access. Make sure that you select the correct
proxy type from the Proxy type  drop-down menu.
drop-down menu.
Once the new WMS server connection has been created, it will be preserved for future QGIS sessions.
Truco
En las direcciones URL del servidor WMS
Asegúrese, al introducir la URL del servidor WMS, que tiene solo la base URL. Por ejemplo, no debe tener fragmentos como request=GetCapabilities o version=1.0.0 en su URL.
Cargando capas WMS/WMTS¶
Una vez que haya llenado exitosamente en sus parámetros, puede utilizar el botón [Conectar] para recuperar las capacidades del servidor seleccionado. Esto incluye la codificación de la imagen, capas, estilos de capa y proyecciones. Como es una operación de la red, la velocidad de respuesta depende de la calidad de la conexión de red al servidor WMS. Mientras descarga los datos desde el servidor WMS, el proceso de descarga se visualizara en la parte inferior izquierda del dialogo WMS.
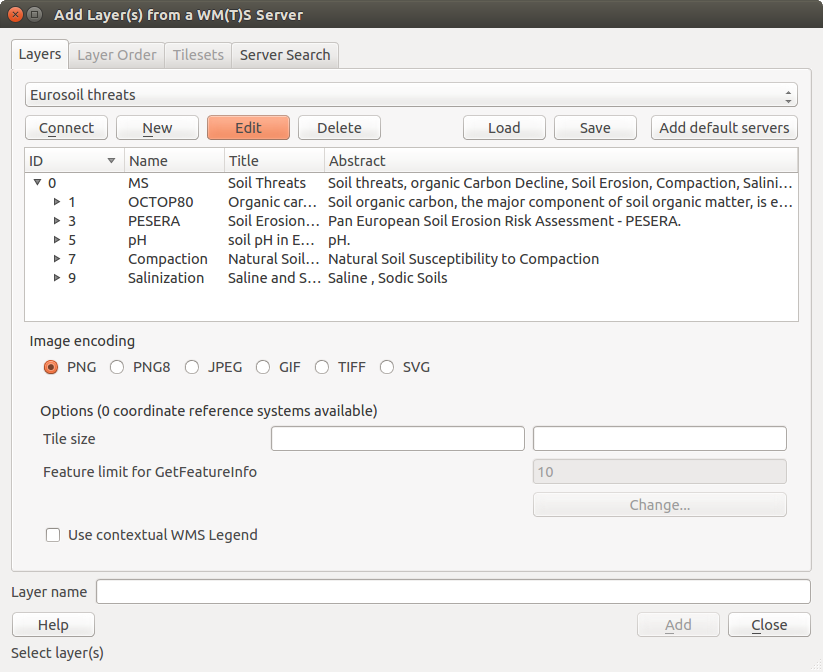
Su pantalla debe ahora lucir un poco como figure_OGR_1, que muestra la respuesta proporcionada por el servidor WMS del European Soil Portal.
Figure OGR 1:
Codificación de la Imagen
La sección Codificación de la imagen lista los formatos que reconoce por ambos el cliente y el servidor. Elija uno dependiendo de sus requerimientos de precisión de imagen.
Truco
Codificación de la Imagen
Normalmente, encontrará que un servidor WMS le ofrece la opción de codificación de la imagen en JPEG o PNG. JPEG es un formato de compresión con pérdida, mientras que PNG reproduce fielmente los datos crudos raster.
Utilizar JPEG si se espera que los datos WMS sean de naturaleza fotográfica y/o no le importa cierta perdida de calidad de la imagen. Esta disyuntiva típicamente reduce en cinco veces la necesidad de transferencia de datos en comparación con PNG.
Utilice PNG si desea representaciones precisas de los datos originales y no le importa el incremento de los requisitos de transferencia de datos.
Opciones
La zona Opciones del diálogo provee un campo de texto donde se puede añadir un Nombre de capa para la capa WMS. Este nombre aparecerá en la leyenda después de cargar la capa.
Debajo del nombre de la capa, se puede definir Tamaño de la tesela, si desea establecer tamaños de tesela (por ejemplo, 256x256) para dividir la petición WMS en múltiples peticiones.
El Límite del objeto espacial para GetFeatureInfo define los objetos espaciales del servidor a consultar.
Si se selecciona un WMS de la lista, aparece un campo con la proyección predeterminada proporcionada por el servidor de mapas. Si el botón [Cambiar...] está activo, puede hacer clic en él y cambiar la proyección por defecto de los WMS a otro SRC proporcionado por el servidor WMS.
Finalmente puede activar  Utiliza leyenda-WMS contextual si el servidor WMS admite este objeto. Entonces sólo la leyenda relevante para su actual extensión de vista de mapa se mostrará y así no incluirá los elementos de la leyenda por cosas que no puede ver en el mapa actual.
Utiliza leyenda-WMS contextual si el servidor WMS admite este objeto. Entonces sólo la leyenda relevante para su actual extensión de vista de mapa se mostrará y así no incluirá los elementos de la leyenda por cosas que no puede ver en el mapa actual.
Orden de la capa
La pestaña Orden de Capas lista las capas seleccionadas disponibles de la conexión actual al servidor WMS. Puede notar que algunas capas son ampliables; esto significa que la capa se puede visualizar en una selección de estilos de imagen.
You can select several layers at once, but only one image style per layer. When several layers are selected, they will be combined at the WMS server and transmitted to QGIS in one go.
Truco
Ordenar capas WMS
Las capas WMS representadas por un servidor son sobrepuestas en el orden listado en la sección de Capas, desde la parte superior a la parte inferior de la lista. Si se desea cambiar el orden de la superposición, se puede usar la pestaña Orden de capas.
Transparencia
In this version of QGIS, the Global transparency setting from the Layer Properties is hard coded to be always on, where available.
Truco
Transparencia de capa WMS
La disponibilidad de imagen WMS transparente depende de la codificación de la imagen utilizada: PNG y GIF reconoce la transparencia, mientras JPEG deja sin reconocerlo.
Sistema de referencia de coordenadas
A coordinate reference system (CRS) is the OGC terminology for a QGIS projection.
Cada capa WMS se puede representar en múltiples SRC’s, dependiendo de la capacidad del servidor WMS.
Para elegir un SRC, seleccione [Cambiar...] y un cuadro de diálogo similar a Figure Projection 3 en Trabajar con Proyecciones aparecerá. La principal diferencia con la versión WMS del diálogo es que sólo aquellos SRCs son reconocidos por el servidor WMS se le mostrarán.
Busqueda del servidor¶
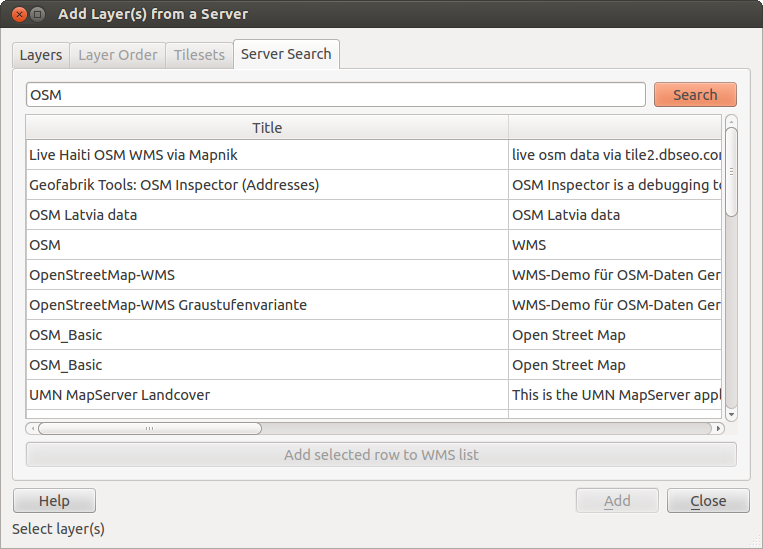
Within QGIS, you can search for WMS servers. Figure_OGC_2 shows the Server Search tab with the Add Layer(s) from a Server dialog.
Figure OGR 2:
As you can see, it is possible to enter a search string in the text field and hit the [Search] button. After a short while, the search result will be populated into the list below the text field. Browse the result list and inspect your search results within the table. To visualize the results, select a table entry, press the [Add selected row to WMS list] button and change back to the Layers tab. QGIS has automatically updated your server list, and the selected search result is already enabled in the list of saved WMS servers in the Layers tab. You only need to request the list of layers by clicking the [Connect] button. This option is quite handy when you want to search maps by specific keywords.
Básicamente, esta opción es una interfaz del API de http://geopole.org.
Conjunto de teselas¶
Al utilizar servicios WMTS (Cached WMS) como
http://opencache.statkart.no/gatekeeper/gk/gk.open_wmts?\
service=WMTS&request=GetCapabilities
you are able to browse through the Tilesets tab given by the server. Additional information like tile size, formats and supported CRS are listed in this table. In combination with this feature, you can use the tile scale slider by selecting Settings ‣ Panels (KDE and Windows) or View ‣ Panels (Gnome and MacOSX), then choosing Tile scale. This gives you the available scales from the tile server with a nice slider docked in.
Utilizar la herramienta de Identificar objetos espaciales¶
Once you have added a WMS server, and if any layer from a WMS server is queryable,
you can then use the  Identify tool to select a pixel on
the map canvas. A query is made to the WMS server for each selection made.
The results of the query are returned in plain text. The formatting of this text
is dependent on the particular WMS server used.
Identify tool to select a pixel on
the map canvas. A query is made to the WMS server for each selection made.
The results of the query are returned in plain text. The formatting of this text
is dependent on the particular WMS server used.
Selección de Formato
Si múltiples formatos de salida son reconocidos por el servidor, una lista desplegable con formatos admitidos se añade automáticamente al diálogo de resultados identificados y el formato seleccionada puede ser almacenado en el proyecto para la capa.
Usar formato GML
The  Identify tool supports WMS server response (GetFeatureInfo) in GML format (it is called Feature in the QGIS GUI in this context). If “Feature” format is supported by the server and selected, results of the Identify tool are vector features, as from a regular vector layer. When a single feature is selected in the tree, it is highlighted in the map and it can be copied to the clipboard and pasted to another vector layer. See the example setup of the UMN Mapserver below to support GetFeatureInfo in GML format.
Identify tool supports WMS server response (GetFeatureInfo) in GML format (it is called Feature in the QGIS GUI in this context). If “Feature” format is supported by the server and selected, results of the Identify tool are vector features, as from a regular vector layer. When a single feature is selected in the tree, it is highlighted in the map and it can be copied to the clipboard and pasted to another vector layer. See the example setup of the UMN Mapserver below to support GetFeatureInfo in GML format.
# in layer METADATA add which fields should be included and define geometry (example):
"gml_include_items" "all"
"ows_geometries" "mygeom"
"ows_mygeom_type" "polygon"
# Then there are two possibilities/formats available, see a) and b):
# a) basic (output is generated by Mapserver and does not contain XSD)
# in WEB METADATA define formats (example):
"wms_getfeatureinfo_formatlist" "application/vnd.ogc.gml,text/html"
# b) using OGR (output is generated by OGR, it is send as multipart and contains XSD)
# in MAP define OUTPUTFORMAT (example):
OUTPUTFORMAT
NAME "OGRGML"
MIMETYPE "ogr/gml"
DRIVER "OGR/GML"
FORMATOPTION "FORM=multipart"
END
# in WEB METADATA define formats (example):
"wms_getfeatureinfo_formatlist" "OGRGML,text/html"
Ver propiedades
Una vez que haya añadido un servidor WMS, puede ver sus propiedades haciendo clic derecho sobre el mismo en la leyenda y la seleccionar Propiedades.
Pestaña de Metadatos
La pestaña Metadatos muestra una gran cantidad de información acerca del servidor WMS, generalmente obtenida de la declaración de capacidades de ese servidor. Muchas definiciones pueden ser extraídas mediante la lectura del estándar WMS (vea OPEN-GEOSPATIAL-CONSORTIUM en Referencias bibliográficas y web), pero aquí hay algunas definiciones útiles:
Propiedades del servidor
Versión WMS — La versión WMS implementada por el servidor.
- Image Formats — The list of MIME-types the server can respond with
when drawing the map. QGIS supports whatever formats the underlying Qt
libraries were built with, which is typically at least
image/pngandimage/jpeg. - Identity Formats — The list of MIME-types the server can respond
with when you use the Identify tool. Currently, QGIS supports the
text-plaintype.
Propiedades de la capa
Seleccionar — Sea o no esta capa seleccionada cuando su servidor fue añadido a este proyecto.
- Visible — Whether or not this layer is selected as visible in the legend (not yet used in this version of QGIS).
Poder Identificar — Sea o no esta capa regresará algunos resultados cuando la herramienta de identificar se utilice en él.
- Can be Transparent — Whether or not this layer can be rendered with
transparency. This version of QGIS will always use transparency if this is
Yesand the image encoding supports transparency. - Can Zoom In — Whether or not this layer can be zoomed in by the server.
This version of QGIS assumes all WMS layers have this set to
Yes. Deficient layers may be rendered strangely. Conteo en Cascada — Los servidores WMS pueden actuar como proxy para otros servidores WMS para obtener datos ráster de una capa. Esta entrada muestra el número de veces que se remitió la solicitud de esta capa para ver a los servidores WMS para obtener un resultado.
- Fixed Width, Fixed Height — Whether or not this layer has fixed source pixel dimensions. This version of QGIS assumes all WMS layers have this set to nothing. Deficient layers may be rendered strangely.
- WGS 84 Bounding Box — The bounding box of the layer, in WGS 84
coordinates. Some WMS servers do not set this correctly (e.g., UTM coordinates
are used instead). If this is the case, then the initial view of this layer
may be rendered with a very ‘zoomed-out’ appearance by QGIS. The WMS webmaster
should be informed of this error, which they may know as the WMS XML elements
LatLonBoundingBox,EX_GeographicBoundingBoxor the CRS:84BoundingBox. Disponible en SRC — Las proyecciones que esta capa puede representar por el servidor WMS. Éstos se enumeran en el formato nativo de WMS.
Disponible en estilo — Los estilos de imagen que esta capa puede representar por el servidor WMS.
Mostrar leyenda gráfica WMS en la tabla de contenido y diseñador de impresión¶
The QGIS WMS data provider is able to display a legend graphic in the table of contents’ layer list and in the map composer. The WMS legend will be shown only if the WMS server has GetLegendGraphic capability and the layer has getCapability url specified, so you additionally have to select a styling for the layer.
Si hay definida una legendGraphic, ésta se mostrará debajo de la capa. Es pequeña y hay que hacer clic sobre ella para abrirla en tamaño real (debido a una limitación de la arquitectura de QgsLegendInterface). Al hacer clic en la leyenda de la capa se abrirá un cuadro con la leyenda a la máxima resolución.
In the print composer, the legend will be integrated at it’s original (dowloaded) dimension. Resolution of the legend graphic can be set in the item properties under Legend -> WMS LegendGraphic to match your printing requirements
La leyenda mostrará información contextual basada en su escala actual. La leyenda WMS se muestra sólo si el servidor WMS tiene capacidad GetLegendGraphic y la capa tiene definida una url getCapability, para lo que se debe seleccionar un estilo.
Limitaciones del cliente WMS¶
Not all possible WMS client functionality had been included in this version of QGIS. Some of the more noteworthy exceptions follow.
Editar la configuración de la capa WMS
Once you’ve completed the  Add WMS layer procedure,
there is no way to change the settings. A work-around is to delete the layer
completely and start again.
Add WMS layer procedure,
there is no way to change the settings. A work-around is to delete the layer
completely and start again.
**Autentificación necesaria en servidores WMS **
Actualmente, se admiten servicios WMS públicamente accesibles y garantizados. Los servidores WMS garantizados se puede acceder mediante autenticación pública. El usuario puede agregar las credenciales (opcional) cuando agregue un servidor WMS. Vea la sección :ref: ogc-wms-servers para más detalles.
Truco
Acceso garantizado a capas OGC
Si necesita acceder a capas protegidas mediante métodos seguros que no sean la autenticación básica, puede utilizar InteProxy como un proxy transparente, lo que lo hace compatible con varios métodos de autenticación. Puede encontrar más información en el manual InteProxy en http://inteproxy.wald.intevation.org.
Truco
QGIS WMS Mapserver
Since Version 1.7.0, QGIS has its own implementation of a WMS 1.3.0 Mapserver. Read more about this in chapter QGIS as OGC Data Server.
WCT Cliente¶
 Un Web Coverage Service (WCS) proporciona acceso a los datos ráster en formas que son útiles para la representación del lado cliente, como datos de entrada en los modelos científicos, y para otros clientes. El WCS se puede comparar con la WFS y el WMS. Como WMS y WFS instancias de servicios, un WCS permite a los clientes elegir partes de las explotaciones de información de un servidor basado en restricciones espaciales y otros criterios de consulta.
Un Web Coverage Service (WCS) proporciona acceso a los datos ráster en formas que son útiles para la representación del lado cliente, como datos de entrada en los modelos científicos, y para otros clientes. El WCS se puede comparar con la WFS y el WMS. Como WMS y WFS instancias de servicios, un WCS permite a los clientes elegir partes de las explotaciones de información de un servidor basado en restricciones espaciales y otros criterios de consulta.
QGIS has a native WCS provider and supports both version 1.0 and 1.1 (which are significantly different), but currently it prefers 1.0, because 1.1 has many issues (i.e., each server implements it in a different way with various particularities).
The native WCS provider handles all network requests and uses all standard QGIS network settings (especially proxy). It is also possible to select cache mode (‘always cache’, ‘prefer cache’, ‘prefer network’, ‘always network’), and the provider also supports selection of time position, if temporal domain is offered by the server.
Cliente WFS y WFS-T¶
In QGIS, a WFS layer behaves pretty much like any other vector layer. You can identify and select features, and view the attribute table. Since QGIS 1.6, editing WFS-T is also supported.
En general, añadir una capa WFS es muy similar al procedimiento utilizado con WMS. La diferencia es que no hay servidores por defecto definidos, así que tenemos que añadir la nuestra.
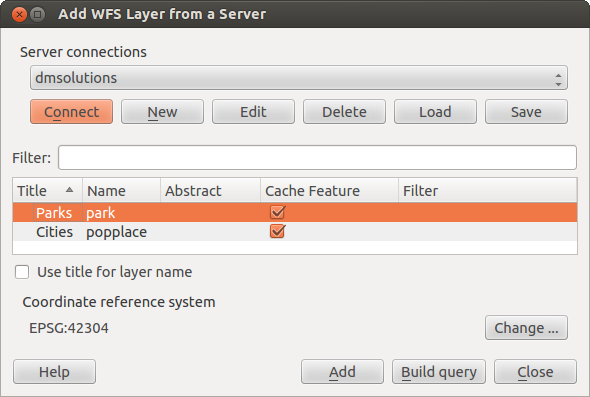
Cargar una capa WFS
Como un ejemplo, utilizamos el servidor WFS de DM Solutions y mostramos una capa. La URL es http://www2.dmsolutions.ca/cgi-bin/mswfs_gmap
Haga clic en la herramienta
 Añadir capa WFS en la barra de herramientas Capas. El diálogo Añadir capa WFS de un servidor aparecera.
Añadir capa WFS en la barra de herramientas Capas. El diálogo Añadir capa WFS de un servidor aparecera.Haga clic en [Nuevo].
Ingrese ‘DS Solutions’ como nombre.
Introducir la URL (véase más arriba).
Haga clic en [Aceptar].
- Choose ‘DM Solutions’ from the Server Connections
 drop-down list.
drop-down list. Haga clic en [Conectar]
Espere a que la capa de capas este poblada.
Seleccione la capa Parks en la lista.
Haga clic en [Aplicar] para añadir la capa al mapa.
Tenga en cuenta que cualquier configuración de proxy que pueda haber establecido en sus preferencias también son reconocidos.
Figure OGR 3:
You’ll notice the download progress is visualized in the lower left of the QGIS main window. Once the layer is loaded, you can identify and select a province or two and view the attribute table.
Sólo la versión 1.0.0 de WFS es compatible. Por ahora, no ha habido muchas pruebas contra versiones WFS implementados en otros servidores de la CMA. Si tiene problemas con cualquier otro servidor WFS, por favor no dude en ponerse en contacto con el equipo de desarrollo. Por favor, consulte la sección :ref: label_helpsupport para más información sobre las listas de correo.
Truco
Encontrar servidores WFS
You can find additional WFS servers by using Google or your favorite search engine. There are a number of lists with public URLs, some of them maintained and some not.