25.1.1. Cartography¶
25.1.1.1. Align points to features¶
Calculates the rotation required to align point features with their nearest feature from another reference layer. A new field is added to the output layer which is filled with the angle (in degrees, clockwise) to the nearest reference feature.
Optionally, the output layer’s symbology can be set to automatically use the calculated rotation field to rotate marker symbols. If desired, a maximum distance to use when aligning points can be set, to avoid aligning isolated points to distant features.
Hint
This algorithm is designed for use cases like aligning building point symbols to follow the nearest road direction.
 Allows features in-place modification
Allows features in-place modification
Parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: point] |
Point features to calculate the rotation for |
Reference layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Layer to find the closest feature from for rotation calculation |
Maximum distance to consider Optional |
|
[number] Default: Not set |
If no reference feature is found within this distance, no rotation is assigned to the point feature. |
Angle field name |
|
[string] Default: ‘rotation’ |
Field in which to store the rotation value. |
Automatically apply symbology |
|
[boolean] Default: True |
Rotates the symbol marker of the features using the angle field value |
Aligned layer |
|
[vector: point] Default: |
Specify the rotated output vector layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Outputs¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Aligned layer |
|
[vector: point] |
The point layer appended with a rotation field. If loaded to QGIS, it is applied by default the input layer symbology, with a data-defined rotation of its marker symbol. |
Python code¶
Algorithm ID: native:angletonearest
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.1.2. Combine style databases¶
Combines multiple QGIS style databases into a single style database. If items of the same type with the same name exist in different source databases these will be renamed to have unique names in the output combined database.
See also
Parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input databases |
|
[file] [list] |
Files containing QGIS style items |
Objects to combine |
|
[enumeration] [list] |
Types of style items in the input databases you would like to put in the new database. These can be:
|
Output style database |
|
[file] Default: |
Output
|
Outputs¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Color ramp count |
|
[number] |
|
Label settings count |
|
[number] |
|
Output style database |
|
[file] |
Output |
Symbol count |
|
[number] |
|
Text format count |
|
[number] |
Python code¶
Algorithm ID: native:combinestyles
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.1.3. Create categorized renderer from styles¶
Sets a vector layer’s renderer to a categorized renderer using matching symbols from a style database. If no style file is specified, symbols from the user’s current symbol library are used instead.
A specified expression or field is used to create categories for the renderer. Each category is individually matched to the symbols which exist within the specified QGIS XML style database. Whenever a matching symbol name is found, the category’s symbol will be set to this matched symbol.
If desired, outputs can also be tables containing lists of the categories which could not be matched to symbols, and symbols which were not matched to categories.
Parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: any] |
Vector layer to apply a categorized style to |
Categorize using expression |
|
[expression] |
Field or expression to categorize the features |
Style database (leave blank to use saved symbols) |
|
[file] |
File ( |
Use case-sensitive match to symbol names |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
If True (checked), applies a case sensitive comparison between the categories and symbols names |
Ignore non-alphanumeric characters while matching |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
If True (checked), non-alphanumeric characters in the categories and symbols names will be ignored, allowing greater tolerance during the match. |
Non-matching categories Optional |
|
[table] Default: |
Output table for categories which do not match any symbol in the database. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Non-matching symbol names Optional |
|
[table] Default: |
Output table for symbols from the provided style database which do not match any category. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Outputs¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Non-matching categories |
|
[table] |
Lists categories which could not be matched to any symbol in the provided style database |
Non-matching symbol names |
|
[table] |
Lists symbols from the provided style database which could not match any category |
Categorized layer |
|
[same as input] |
The input vector layer with the categorized style applied. No new layer is output. |
Python code¶
Algorithm ID: native:categorizeusingstyle
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.1.4. Create style database from project¶
Extracts all style objects (symbols, color ramps, text formats and label settings) from a QGIS project.
The extracted symbols are saved to a QGIS style database (XML format),
which can be managed and imported via the Style Manager
dialog.
See also
Parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input project (leave blank to use current) Optional |
|
[file] |
A QGIS project file to extract the style items from |
Objects to extract |
|
[enumeration] [list] |
Types of style items in the input project you would like to put in the new database. These can be:
|
Output style database |
|
[file] Default: |
Specify the output
|
Outputs¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Color ramp count |
|
[number] |
Number of color ramps |
Label settings count |
|
[number] |
Number of label settings |
Output style database |
|
[file] |
Output |
Symbol count |
|
[number] |
Number of symbols |
Text format count |
|
[number] |
Number of text formats |
Python code¶
Algorithm ID: native:stylefromproject
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.1.5. Export atlas layout as image¶
Exports the atlas of a print layout as image files (e.g. PNG or JPEG images).
If a coverage layer is set, the selected layout’s atlas settings exposed in this algorithm will be overwritten. In this case, an empty filter or sort by expression will turn those settings off.
Parameters¶
Basic parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Atlas layout |
|
[layout] |
Layout to export |
Coverage layer Optional |
|
[vector: any] |
Layer to use to generate the atlas |
Filter expression |
|
[expression] |
Expression to use to filter out atlas features |
Sort expression Optional |
|
[expression] |
Expression to use to sort the atlas features |
Reverse sort order Optional |
|
[boolean] |
Determines if sorting should be inverted. Used when a sort expression is provided. |
Output filename expression |
|
[expression] Default: ‘output_’||@atlas_featurenumber |
Expression for use to generate filenames |
Output folder |
|
[folder] |
Destination folder where the images will be generated |
Advanced parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Map layers to assign to unlocked map item(s) Optional |
|
[enumeration] [layer] |
Layers to display in the map item(s) whose contents are not locked |
Image format |
|
[list] Default: png |
File format of the generated output(s). The list of available formats varies depending on OS and installed drivers. |
DPI Optional |
Default: Not set |
[number] |
DPI of the output file(s). If not set, the value in the print layout settings will be used. |
Generate world file |
|
[boolean] Default: True |
Determines if a world file should be generated |
Export RDF metadata |
|
[boolean] Default: True |
Determines if RDF metadata (title, author, …) should be generated |
Enable antialiasing |
|
[boolean] Default: True |
Determines if antialiasing should be enabled |
Outputs¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Image file |
|
[file] |
Image files generated by the atlas layout |
Python code¶
Algorithm ID: native:atlaslayouttoimage
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.1.6. Export atlas layout as PDF¶
Exports the atlas of a print layout as a PDF file(s).
If a coverage layer is set, the selected layout’s atlas settings exposed in this algorithm will be overwritten. In this case, an empty filter or sort by expression will turn those settings off.
Parameters¶
Basic parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Atlas layout |
|
[layout] |
Layout to export |
Coverage layer Optional |
|
[vector: any] |
Layer to use to generate the atlas |
Filter expression |
|
[expression] |
Expression to use to filter out atlas features |
Sort expression Optional |
|
[expression] |
Expression to use to sort the atlas features |
Reverse sort order Optional |
|
[boolean] |
Determines if sorting should be inverted. Used when a sort expression is provided. |
Advanced parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Map layers to assign to unlocked map item(s) Optional |
|
[enumeration] [layer] |
Layers to display in the map item(s) whose contents are not locked |
DPI Optional |
Default: Not set |
[number] |
DPI of the output file(s). If not set, the value in the print layout settings will be used. |
Always export as vectors |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
Determines if vectorial data should be left as vectors |
Append georeference information |
|
[boolean] Default: True |
Determines if a world file should be generated |
Export RDF metadata |
|
[boolean] Default: True |
Determines if RDF metadata (title, author, …) should be generated |
Disable tiled raster layer exports |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
Determines if raster should be tiled |
Simplify geometries to reduce output file size |
|
[boolean] Default: True |
Determines if geometries should be simplified to reduce output file size |
Text export |
|
[list] Default: 0 |
Determines if text should be exported as path or text objects. Possible options are:
|
PDF file |
|
[file] Default: [Save to temporary file] |
Name (including path) of the output file. One of:
|
Outputs¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
PDF file |
|
[file] |
PDF file corresponding to the exported atlas layout |
Python code¶
Algorithm ID: native:atlaslayouttopdf
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.1.7. Export print layout as image¶
Exports a print layout as an image file (e.g. PNG or JPEG images)
Parameters¶
Basic parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Print layout |
|
[layout] |
Layout to export |
Image file |
|
[file] Default: [Save to temporary file] |
Name (including path) of the output file. One of:
|
Advanced parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Map layers to assign to unlocked map item(s) Optional |
|
[enumeration] [layer] |
Layers to display in the map item(s) whose contents are not locked |
DPI Optional |
Default: Not set |
[number] |
DPI of the output file(s). If not set, the value in the print layout settings will be used. |
Generate world file |
|
[boolean] Default: True |
Determines if a world file should be generated |
Export RDF metadata |
|
[boolean] Default: True |
Determines if RDF metadata (title, author, …) should be generated |
Enable antialiasing |
|
[boolean] Default: True |
Determines if antialiasing should be enabled |
Outputs¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Image file |
|
[file] |
Image file corresponding to the exported print layout |
Python code¶
Algorithm ID: native:printlayouttoimage
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.1.8. Export print layout as pdf¶
Exports a print layout as a PDF file.
Parameters¶
Basic parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Print Layout |
|
[layout] |
Layout to export |
PDF file |
|
[file] Default: [Save to temporary file] |
Name (including path) of the output file. One of:
|
Advanced parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Map layers to assign to unlocked map item(s) Optional |
|
[enumeration] [layer] |
Layers to display in the map item(s) whose contents are not locked |
DPI Optional |
Default: Not set |
[number] |
DPI of the output file(s). If not set, the value in the print layout settings will be used. |
Always export as vectors |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
Determines if vectorial data should be left as vectors |
Append georeference information |
|
[boolean] Default: True |
Determines if a world file should be generated |
Export RDF metadata |
|
[boolean] Default: True |
Determines if RDF metadata (title, author, …) should be generated |
Disable tiled raster layer exports |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
Determines if raster should be tiled |
Simplify geometries to reduce output file size |
|
[boolean] Default: True |
Determines if geometries should be simplified to reduce output file size |
Text export |
|
[list] Default: 0 |
Determines if text should be exported as path or text objects. Possible options are:
|
Export layers as separate PDF files |
|
[boolean] Default: False |
If True, then a separate PDF file will be created per layer per map item in the layout. Additionally, separate PDF files may be created for other complex layout items, resulting in a set of PDF files which contain logical atomic components of the layout. |
Outputs¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
PDF file |
|
[file] |
PDF file(s) corresponding to the exported print layout |
Python code¶
Algorithm ID: native:printlayouttopdf
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.1.9. Print layout map extent to layer¶
Creates a polygon layer containing the extent of a print layout map item (or items), with attributes specifying the map size (in layout units, i.e. the reference map units), scale and rotation.
If the map item parameter is specified, then only the matching map extent will be exported. If it is not specified, all map extents from the layout will be exported.
Optionally, a specific output CRS can be specified. If it is not specified, the original map item CRS will be used.
Parameters¶
Basic parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Print layout |
|
[enumeration] |
A print layout in the current project |
Map item Optional |
|
[enumeration] Default: All the map items |
The map item(s) whose information you want to extract. If none is provided then all the map items are processed. |
Extent |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
Specify the output vector layer for the extent(s). One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Advanced parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Overrride CRS Optional |
|
[crs] Default: The layout CRS |
Select the CRS for the layer in which the information will be reported. |
Outputs¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Map height |
|
[number] |
|
Extent |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Output polygon vector layer containing extents of all the input layout map item(s) |
Map rotation |
|
[number] |
|
Map scale |
|
[number] |
|
Map width |
|
[number] |
Python code¶
Algorithm ID: native:printlayoutmapextenttolayer
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.1.10. Set layer style¶
Applies a provided style to a layer. The style must be defined in a
QML file.
No new output are created: the style is immediately assigned to the layer.
Parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input Layer |
|
[layer] |
Input layer you want to apply the style to |
Style file |
|
[file] |
Path to the |
Outputs¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
[same as input] |
The input layer with the new style assigned. No new layer is created. |
Python code¶
Algorithm ID: native:setlayerstyle
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.
25.1.1.11. Topological coloring¶
Assigns a color index to polygon features in such a way that no adjacent polygons share the same color index, whilst minimizing the number of colors required.
The algorithm allows choice of method to use when assigning colors.
A minimum number of colors can be specified if desired. The color index is saved to a new attribute named color_id.
The following example shows the algorithm with four different colors chosen; as you can see each color class has the same amount of features.
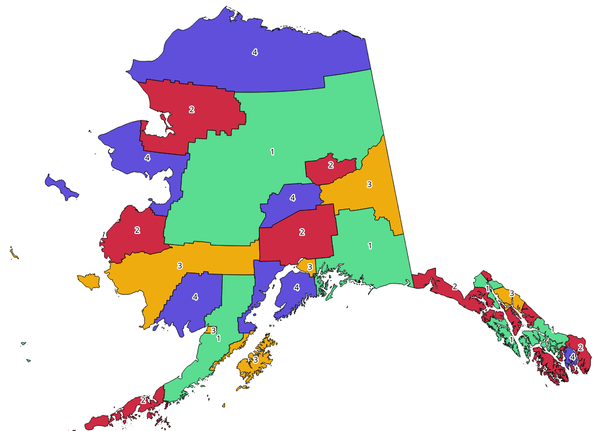
Fig. 25.1 Topological colors example¶
Parameters¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Input layer |
|
[vector: polygon] |
The input polygon layer |
Minimum number of colors |
|
[number] Default: 4 |
The minimum number of colors to assign. Minimum 1, maximum 1000. |
Minimum distance between features |
|
[number] Default: 0.0 |
Prevent nearby (but non-touching) features from being assigned equal colors. Minimum 0.0. |
Balance color assignment |
|
[enumeration] Default: 0 |
Options are:
|
Colored |
|
[vector: polygon] Default: |
Specify the output layer. One of:
The file encoding can also be changed here. |
Outputs¶
Label |
Name |
Type |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
Colored |
|
[vector: polygon] |
Polygon vector layer with an added |
Python code¶
Algorithm ID: qgis:topologicalcoloring
import processing
processing.run("algorithm_id", {parameter_dictionary})
The algorithm id is displayed when you hover over the algorithm in the Processing Toolbox. The parameter dictionary provides the parameter NAMEs and values. See Using processing algorithms from the console for details on how to run processing algorithms from the Python console.