Os <i>snippets</i> de código nesta página precisam das seguintes importações se estiver fora da console pyqgis:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | from qgis.core import (
QgsApplication,
QgsRasterLayer,
QgsAuthMethodConfig,
QgsDataSourceUri,
QgsPkiBundle,
QgsMessageLog,
)
from qgis.gui import (
QgsAuthAuthoritiesEditor,
QgsAuthConfigEditor,
QgsAuthConfigSelect,
QgsAuthSettingsWidget,
)
from qgis.PyQt.QtWidgets import (
QWidget,
QTabWidget,
)
from qgis.PyQt.QtNetwork import QSslCertificate
|
14. Infraestrutura de autenticação¶
14.1. Introdução¶
User reference of the Authentication infrastructure can be read in the User Manual in the Authentication System Overview paragraph.
This chapter describes the best practices to use the Authentication system from a developer perspective.
The authentication system is widely used in QGIS Desktop by data providers whenever credentials are required to access a particular resource, for example when a layer establishes a connection to a Postgres database.
There are also a few widgets in the QGIS gui library that plugin developers can use to easily integrate the authentication infrastructure into their code:
A good code reference can be read from the authentication infrastructure tests code.
Aviso
Due to the security constraints that were taken into account during the authentication infrastructure design, only a selected subset of the internal methods are exposed to Python.
14.2. Glossário¶
Aqui estão algumas definições dos objetos mais comuns tratados neste capítulo.
- Palavra-passe Mestre
Palavra-passe para permitir o acesso e a desencriptação da credencial guardada na BD de autenticação de QGIS
- Base de Dados de Autenticação
A Master Password crypted sqlite db
qgis-auth.dbwhere Authentication Configuration are stored. e.g user/password, personal certificates and keys, Certificate Authorities- BD de Autenticação
- Configuração da Autenticação
A set of authentication data depending on Authentication Method. e.g Basic authentication method stores the couple of user/password.
- Configurar Autenticação
- Método de Autenticação
A specific method used to get authenticated. Each method has its own protocol used to gain the authenticated level. Each method is implemented as shared library loaded dynamically during QGIS authentication infrastructure init.
14.3. O ponto de entrada de QgsAuthManager¶
The QgsAuthManager singleton
is the entry point to use the credentials stored in the QGIS encrypted
Authentication DB, i.e. the qgis-auth.db file under the
active user profile folder.
This class takes care of the user interaction: by asking to set a master password or by transparently using it to access encrypted stored information.
14.3.1. Inicializar o gestor e definir a palavra-passe mestra¶
The following snippet gives an example to set master password to open the access to the authentication settings. Code comments are important to understand the snippet.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | authMgr = QgsApplication.authManager()
# check if QgsAuthManager has already been initialized... a side effect
# of the QgsAuthManager.init() is that AuthDbPath is set.
# QgsAuthManager.init() is executed during QGIS application init and hence
# you do not normally need to call it directly.
if authMgr.authenticationDatabasePath():
# already initialized => we are inside a QGIS app.
if authMgr.masterPasswordIsSet():
msg = 'Authentication master password not recognized'
assert authMgr.masterPasswordSame("your master password"), msg
else:
msg = 'Master password could not be set'
# The verify parameter checks if the hash of the password was
# already saved in the authentication db
assert authMgr.setMasterPassword("your master password",
verify=True), msg
else:
# outside qgis, e.g. in a testing environment => setup env var before
# db init
os.environ['QGIS_AUTH_DB_DIR_PATH'] = "/path/where/located/qgis-auth.db"
msg = 'Master password could not be set'
assert authMgr.setMasterPassword("your master password", True), msg
authMgr.init("/path/where/located/qgis-auth.db")
|
14.3.2. Preencher authdb com uma nova entrada de «Configuração de Autenticação»¶
Any stored credential is a Authentication Configuration instance of the
QgsAuthMethodConfig
class accessed using a unique string like the following one:
authcfg = 'fm1s770'
that string is generated automatically when creating an entry using the QGIS API or GUI, but it might be useful to manually set it to a known value in case the configuration must be shared (with different credentials) between multiple users within an organization.
QgsAuthMethodConfig is the base class
for any Authentication Method.
Any Authentication Method sets a configuration hash map where authentication
information will be stored. Hereafter a useful snippet to store PKI-path
credentials for a hypothetical alice user:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | authMgr = QgsApplication.authManager()
# set alice PKI data
config = QgsAuthMethodConfig()
config.setName("alice")
config.setMethod("PKI-Paths")
config.setUri("https://example.com")
config.setConfig("certpath", "path/to/alice-cert.pem" )
config.setConfig("keypath", "path/to/alice-key.pem" )
# check if method parameters are correctly set
assert config.isValid()
# register alice data in authdb returning the ``authcfg`` of the stored
# configuration
authMgr.storeAuthenticationConfig(config)
newAuthCfgId = config.id()
assert newAuthCfgId
|
14.3.2.1. Métodos de «Autenticação» disponíveis¶
Authentication Method libraries are loaded dynamically during authentication manager init. Available authentication methods are:
Autenticação de palavra-passe e Utilizador
BásicoEsri-TokenESRI token based authenticationIdentity-CertIdentity certificate authenticationAutenticação de OAuth2
OAuth2Autenticação de caminhos PKI
PKI-PathsAutenticação de PKI PKCS#12
PKI-PKCS#12
14.3.2.2. Preencher Autoridades¶
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | authMgr = QgsApplication.authManager()
# add authorities
cacerts = QSslCertificate.fromPath( "/path/to/ca_chains.pem" )
assert cacerts is not None
# store CA
authMgr.storeCertAuthorities(cacerts)
# and rebuild CA caches
authMgr.rebuildCaCertsCache()
authMgr.rebuildTrustedCaCertsCache()
|
14.3.2.3. Manage PKI bundles with QgsPkiBundle¶
A convenience class to pack PKI bundles composed on SslCert, SslKey and CA
chain is the QgsPkiBundle
class. Hereafter a snippet to get password protected:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | # add alice cert in case of key with pwd
caBundlesList = [] # List of CA bundles
bundle = QgsPkiBundle.fromPemPaths( "/path/to/alice-cert.pem",
"/path/to/alice-key_w-pass.pem",
"unlock_pwd",
caBundlesList )
assert bundle is not None
# You can check bundle validity by calling:
# bundle.isValid()
|
Refer to QgsPkiBundle class documentation
to extract cert/key/CAs from the bundle.
14.3.3. Remover uma entrada de authdb¶
We can remove an entry from Authentication Database using it’s
authcfg identifier with the following snippet:
authMgr = QgsApplication.authManager()
authMgr.removeAuthenticationConfig( "authCfg_Id_to_remove" )
14.3.4. Leave authcfg expansion to QgsAuthManager¶
The best way to use an Authentication Config stored in the
Authentication DB is referring it with the unique identifier
authcfg. Expanding, means convert it from an identifier to a complete
set of credentials.
The best practice to use stored Authentication Configs, is to leave it
managed automatically by the Authentication manager.
The common use of a stored configuration is to connect to an authentication
enabled service like a WMS or WFS or to a DB connection.
Nota
Take into account that not all QGIS data providers are integrated with the
Authentication infrastructure. Each authentication method, derived from the
base class QgsAuthMethod
and support a different set of Providers. For example the certIdentity() method supports the following list
of providers:
authM = QgsApplication.authManager()
print(authM.authMethod("Identity-Cert").supportedDataProviders())
Saída de amostra:
['ows', 'wfs', 'wcs', 'wms', 'postgres']
For example, to access a WMS service using stored credentials identified with
authcfg = 'fm1s770', we just have to use the authcfg in the data source
URL like in the following snippet:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | authCfg = 'fm1s770'
quri = QgsDataSourceUri()
quri.setParam("layers", 'usa:states')
quri.setParam("styles", '')
quri.setParam("format", 'image/png')
quri.setParam("crs", 'EPSG:4326')
quri.setParam("dpiMode", '7')
quri.setParam("featureCount", '10')
quri.setParam("authcfg", authCfg) # <---- here my authCfg url parameter
quri.setParam("contextualWMSLegend", '0')
quri.setParam("url", 'https://my_auth_enabled_server_ip/wms')
rlayer = QgsRasterLayer(str(quri.encodedUri(), "utf-8"), 'states', 'wms')
|
In the upper case, the wms provider will take care to expand authcfg
URI parameter with credential just before setting the HTTP connection.
Aviso
The developer would have to leave authcfg expansion to the QgsAuthManager, in this way he will be sure that expansion is not done too early.
Usually an URI string, built using the QgsDataSourceURI
class, is used to set a data source in the following way:
authCfg = 'fm1s770'
quri = QgsDataSourceUri("my WMS uri here")
quri.setParam("authcfg", authCfg)
rlayer = QgsRasterLayer( quri.uri(False), 'states', 'wms')
Nota
The False parameter is important to avoid URI complete expansion of the
authcfg id present in the URI.
14.3.4.1. Exemplos de PKI com outros provedores de dados¶
Other example can be read directly in the QGIS tests upstream as in test_authmanager_pki_ows or test_authmanager_pki_postgres.
14.4. Adaptar <i>plug-ins</i> para utilizar a infraestrutura de «Autenticação»¶
Many third party plugins are using httplib2 or other Python networking libraries to manage HTTP
connections instead of integrating with QgsNetworkAccessManager
and its related Authentication Infrastructure integration.
To facilitate this integration a helper Python function has been created
called NetworkAccessManager. Its code can be found here.
Esta classe auxiliar pode ser utilizada como no seguinte <i>snippet</i>:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | http = NetworkAccessManager(authid="my_authCfg", exception_class=My_FailedRequestError)
try:
response, content = http.request( "my_rest_url" )
except My_FailedRequestError, e:
# Handle exception
pass
|
14.5. GUIs de Autenticação¶
In this paragraph are listed the available GUIs useful to integrate authentication infrastructure in custom interfaces.
14.5.1. GUI para selecionar as credenciais¶
If it’s necessary to select a Authentication Configuration from the set
stored in the Authentication DB it is available in the GUI class
QgsAuthConfigSelect.
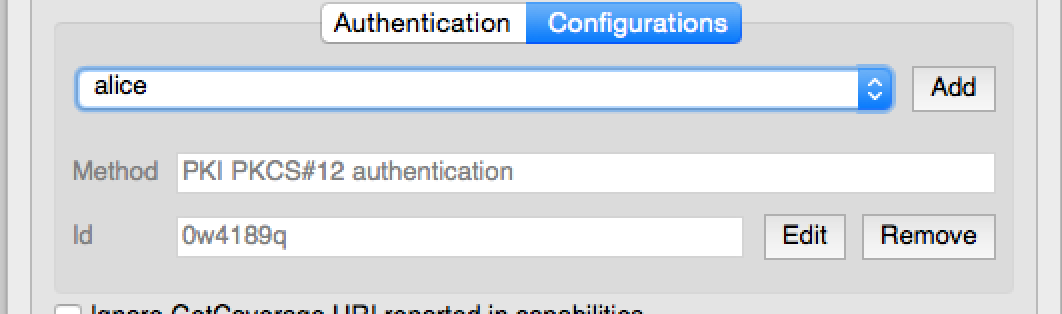
e pode ser utilizada como no seguinte <i>snippet</i>:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | # create the instance of the QgsAuthConfigSelect GUI hierarchically linked to
# the widget referred with `parent`
parent = QWidget() # Your GUI parent widget
gui = QgsAuthConfigSelect( parent, "postgres" )
# add the above created gui in a new tab of the interface where the
# GUI has to be integrated
tabGui = QTabWidget()
tabGui.insertTab( 1, gui, "Configurations" )
|
The above example is taken from the QGIS source code. The second parameter of the GUI constructor refers to data provider type. The parameter is used to restrict the compatible Authentication Methods with the specified provider.
14.5.2. GUI do Editor de Autenticação¶
The complete GUI used to manage credentials, authorities and to access to
Authentication utilities is managed by the
QgsAuthEditorWidgets class.
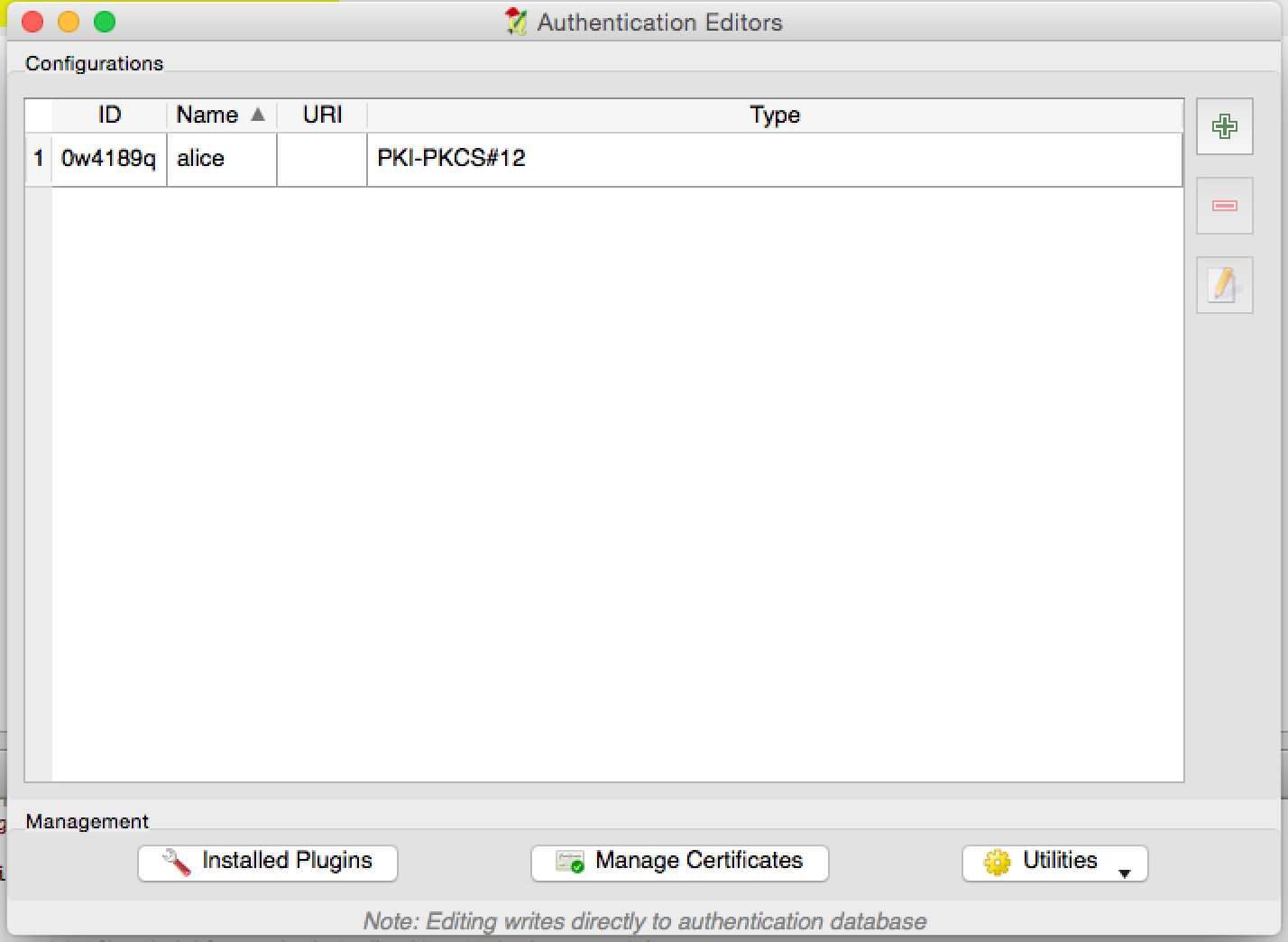
e pode ser utilizada como no seguinte <i>snippet</i>:
1 2 3 4 5 | # create the instance of the QgsAuthEditorWidgets GUI hierarchically linked to
# the widget referred with `parent`
parent = QWidget() # Your GUI parent widget
gui = QgsAuthConfigSelect( parent )
gui.show()
|
An integrated example can be found in the related test.
14.5.3. GUI do Editor de Autoridades¶
A GUI used to manage only authorities is managed by the
QgsAuthAuthoritiesEditor class.
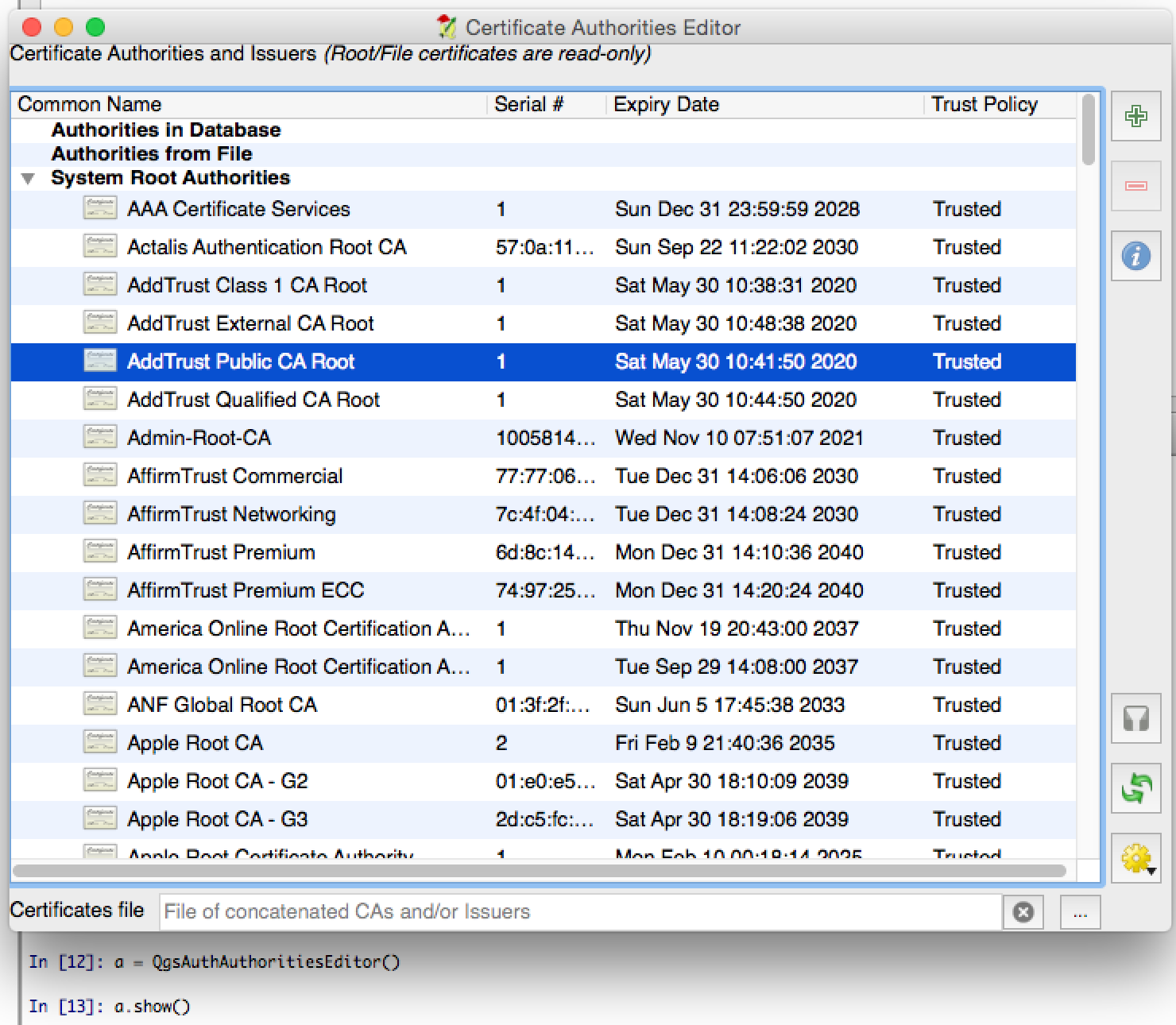
e pode ser utilizada como no seguinte <i>snippet</i>:
1 2 3 4 5 | # create the instance of the QgsAuthAuthoritiesEditor GUI hierarchically
# linked to the widget referred with `parent`
parent = QWidget() # Your GUI parent widget
gui = QgsAuthAuthoritiesEditor( parent )
gui.show()
|