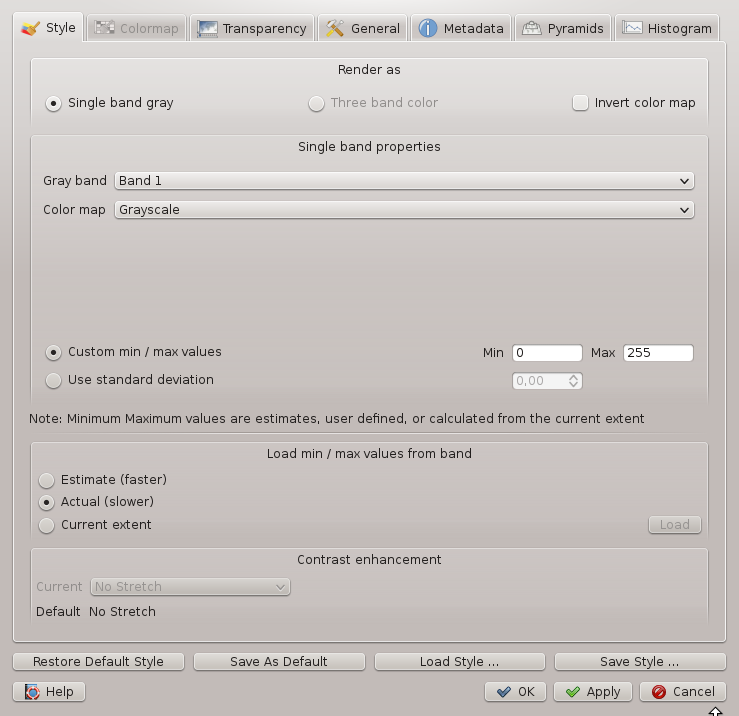
Raster Properties Dialog¶
To view and set the properties for a raster layer, double click on the layer name in the map legend or right click on the layer name and choose Properties from the context menu:
This will open the Raster Layer Properties dialog, (see figure_raster_1).
There are several tabs on the dialog:
- Style
- Transparency
- Colormap
- General
- Metadata
- Pyramids
- Histogram
Figure Raster 1:
Style Tab¶
QGIS can render raster layers in two different ways:
- Single band - one band of the image will be rendered as gray or in pseudocolor or a freak out.
- Three band color - three bands from the image will be rendered, each band representing the red, green or blue component that will be used to create a color image.
Within both render types you can invert the color output using the
 Invert color map checkbox.
Invert color map checkbox.
Single Band Rendering
This selection offers you two possibilites to choose. At first you can select which band you like to use for rendering (if the dataset has more than one band).
The second option offers a selection of available colortables for rendering.
The following settings are available through the dropdownbox
Color map 
- Grayscale (default)
- Pseudocolor
- Freak Out
- Colormap
When selecting the entry ‘Colormap’ from Color map  combobox, the tab Colormap becomes available. For more information
see Colormap.
combobox, the tab Colormap becomes available. For more information
see Colormap.
QGIS can restrict the data displayed to only show cells whose values are within a given number of standard deviations of the mean for the layer.
This is useful when you have one or two cells with abnormally high values in a raster grid that are having a negative impact on the rendering of the raster. This option is only available for pseudocolor and freak out images.
Three band color
This selection offers you a wide range of options to modify the appearance of your rasterlayer. For example you could switch color-bands from the standard RGB-order to something else.
Also scaling of colors are available.
Tip
Viewing a Single Band of a Multiband Raster
If you want to view a single band (for example Red) of a multiband image, you might think you would set the Green and Blue bands to “Not Set”. But this is not the correct way. To display the Red band, set the image type to grayscale, then select Red as the band to use for Gray.
Contrast enhancement
Note
When adding GRASS rasters the option Contrast enhancement will be always set to automatically to stretch to min max regardless if the Quantum GIS general options this is set to another value.
Transparency Tab¶
QGIS has the ability to display each raster layer at varying transparency levels. Use the transparency slider to indicate to what extent the underlying layers (if any) should be visible though the current raster layer. This is very useful, if you like to overlay more than one rasterlayer, e.g. a shaded relief map overlayed by a classified rastermap. This will make the look of the map more three dimensional.
Additionally you can enter a rastervalue, which should be treated as NODATA.
This can be done manually or with the  Add values from
display icon.
Add values from
display icon.
An even more flexible way to customize the transparency can be done in the Custom transparency options section. The transparency of every pixel can be set here.
As an example we want to set the water of our example raster file landcover.tif to a transparency of 20 %. The following steps are neccessary:
- Load the rasterfile landcover.
- Open the Properties dialog by double-clicking on the raster name in the legend or by right-clicking and choosing Properties from the popup menu.
- Select the Transparency tab
- Click the
 Add values manually
button. A new row will appear in the pixel-list.
Add values manually
button. A new row will appear in the pixel-list. - Enter the raster-value (we use 0 here) and adjust the transparency to 20 %.
- Press the [Apply] button and have a look at the map.
You can repeat the steps 4 and 5 to adjust more values with custom transparency.
As you can see this is quite easy to set custom transparency, but it can be
quite a lot of work. Therefore you can use the button  Export to file to save your transparency list to a file. The button
Export to file to save your transparency list to a file. The button
 Import from file loads your transparency settings and
applies them to the current raster layer.
Import from file loads your transparency settings and
applies them to the current raster layer.
Colormap¶
The Colormap tab is only available, when you have selected a singleband rendering within the Style tab (see Style Tab).
Three ways of color interpolation are available:
- Discrete
- Linear
- Exact
The button [Add Entry] adds a color to the individual color table. Button [Delete Entry] deletes a color from the individual color table and the [Sort] button sorts the color table according to the pixel values in the value column. Double clicking on the value-column lets you insert a specific value. Double clicking on the color-column opens the dialog Select color where you can select a color to apply on that value. Further you can also add labels for each color but this value won’t be displayed when you use the identify feature tool.
You can also click on the button  Load color map from band,
which tries to load the table from the band (if it has any). And you can use the
buttons
Load color map from band,
which tries to load the table from the band (if it has any). And you can use the
buttons  Load color map from file or
Load color map from file or  Export color map to file to load an existing color table or to save the
defined color table for other sessions.
Export color map to file to load an existing color table or to save the
defined color table for other sessions.
The block Generate new color map allows you to create newly
categorized colormaps. You only need to select the number of entries
 and press the button Classify. Currently
only one Classification mode
and press the button Classify. Currently
only one Classification mode  is supported - ‘Equal interval’
is supported - ‘Equal interval’
General Tab¶
The General tab displays basic information about the selected raster, including the layer source and display name in the legend (which can be modified). This tab also shows a thumbnail of the layer, its legend symbol, and the palette.
Additionally scale-dependent visibility can be set in this tab. You need to check the checkbox and set an appropriate scale where your data will be displayed in the map canvas.
Also the coordinate reference system (CRS) is printed here as a PROJ.4-string. This can be modified by hitting the [Specify] button.
Metadata Tab¶
The Metadata tab displays a wealth of information about the raster layer, including statistics about each band in the current raster layer. Statistics are gathered on a ‘need to know’ basis, so it may well be that a given layers statistics have not yet been collected.
This tab is mainly for information. You cannot change any values printed inside this tab.
Pyramids Tab¶
Large resolution raster layers can slow navigation in QGIS. By creating lower resolution copies of the data (pyramids), performance can be considerably improved as QGIS selects the most suitable resolution to use depending on the level of zoom.
You must have write access in the directory where the original data is stored to build pyramids.
Several resampling methods can be used to calculate the pyramids:
- Average
- Nearest Neighbour
When checking the checkbox  Build pyramids internally if possible
QGIS tries to build pyramids internally.
Build pyramids internally if possible
QGIS tries to build pyramids internally.
Please note that building pyramids may alter the original data file and once created they cannot be removed. If you wish to preserve a ‘non-pyramided’ version of your raster, make a backup copy prior to building pyramids.
Histogram Tab¶
The Histogram tab allows you to view the distribution of the bands
or colors in your raster. It is generated automaticaly when you open
Histogram tab. All existing bands will be displayed together. You can
save the histogram as an image with the  button.
button.