.
Podstawowe narzędzia¶
Skróty klawiaturowe¶
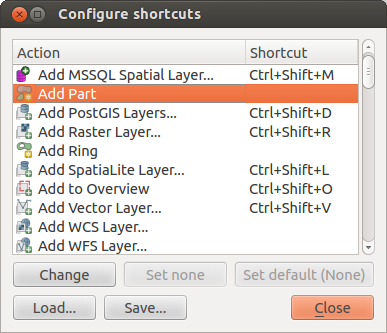
QGIS provides default keyboard shortcuts for many features. You can find them in section Pasek menu. Additionally, the menu option Settings ‣ Configure Shortcuts.. allows you to change the default keyboard shortcuts and to add new keyboard shortcuts to QGIS features.
Figure Shortcuts 1:
Configuration is very simple. Just select a feature from the list and click on [Change], [Set none] or [Set default]. Once you have finished your configuration, you can save it as an XML file and load it to another QGIS installation.
Pomoc kontekstowa¶
Gdy potrzebna ci pomoc w pewnym temacie, możesz skorzystać z pomocy kontekstowej, dostępnej w większości okien dialogowych pod przyciskiem [Pomoc] — proszę zwrócić uwagę, że wtyczki mogą wskazywać na poświęcone im strony internetowe.
Renderowanie¶
By default, QGIS renders all visible layers whenever the map canvas is refreshed. The events that trigger a refresh of the map canvas include:
Dodawanie warstwy
Przesuwanie widoku i przybliżanie
- Resizing the QGIS window
Zmiana widoczności warstwy lub warstw
QGIS allows you to control the rendering process in a number of ways.
Renderowanie zależne od skali¶
Renderowanie zależne od skali pozwala na określenie minimalnej i maksymalnej skali, pomiędzy którymi warstwa jest widoczna. Aby wybrać renderowanie zależne od skali otwórz okno dialogowe Właściwości poprzez dwukrotne kliknięcie na warstwie w legendzie. W zakładce Ogólne zaznacz pole wyboru  Widoczność zależna od skali, a następnie podaj minimalną i maksymalną skalę.
Widoczność zależna od skali, a następnie podaj minimalną i maksymalną skalę.
You can determine the scale values by first zooming to the level you want to use and noting the scale value in the QGIS status bar.
Sterowanie renderowaniem mapy¶
Map rendering can be controlled in the various ways, as described below.
Zawieszanie renderowania¶
To suspend rendering, click the  Render checkbox in the
lower right corner of the status bar. When the
Render checkbox in the
lower right corner of the status bar. When the  Render
checkbox is not checked, QGIS does not redraw the canvas in response to any of
the events described in section Renderowanie. Examples of when you
might want to suspend rendering include:
Render
checkbox is not checked, QGIS does not redraw the canvas in response to any of
the events described in section Renderowanie. Examples of when you
might want to suspend rendering include:
Dodanie wielu warstw i nadanie im stylu przed ich wyświetleniem
Dodanie jednej lub więcej dużych warstw i ustawienie wyświetlania zależnego od skali przed ich wyświetleniem
Dodanie jednej lub więcej większych warstw i przybliżenie się do pewnego widoku przed ich wyświetleniem
Dowolna kombinacja powyższych
Zaznacznie pola wyboru  Renderuj włącza renderowanie i powoduje natychmiastowe odświeżenie kanwy mapy.
Renderuj włącza renderowanie i powoduje natychmiastowe odświeżenie kanwy mapy.
Ustawienia dodawania warstw¶
Można ustawić opcję ładowania warstw bez ich renderowania. Oznacza to, że warstwa zostanie załadowana do mapy, ale jej pole wyboru widoczności bedzie domyślnie odznaczone. Aby ustawić tę opcję wybierz polecenie menu Ustawienia ‣ Opcje i kliknij zakładkę Renderowanie. Odznacz pole wyboru  Domyślnie nowo dodawane warstwy są wyświetlane. Teraz każda nowo dodana do mapy warstwa będzie domyślnie wyłączona (niewidoczna).
Domyślnie nowo dodawane warstwy są wyświetlane. Teraz każda nowo dodana do mapy warstwa będzie domyślnie wyłączona (niewidoczna).
Zatrzymywanie renderowania¶
Do zatrzymania rysowania mapy używaj klawisza ESC . Zatrzymuje on odświeżanie kanwy mapy i pozostawia ją częściowo przerysowaną. Zatrzymanie renderowania mapy może nastąpić po jakimś czasie od naciśnięcia klawisza ESC.
Informacja
W chwili obecnej nie można zatrzymać renderowania — ze względu na problemy interfejsu użytkownika (UI) zostało to zablokowane w porcie Qt4.
Updating the Map Display During Rendering¶
You can set an option to update the map display as features are drawn. By default, QGIS does not display any features for a layer until the entire layer has been rendered. To update the display as features are read from the datastore, choose menu option Settings ‣ Options and click on the Rendering tab. Set the feature count to an appropriate value to update the display during rendering. Setting a value of 0 disables update during drawing (this is the default). Setting a value too low will result in poor performance, as the map canvas is continually updated during the reading of the features. A suggested value to start with is 500.
Zmiana jakości renderowania¶
To influence the rendering quality of the map, you have two options. Choose menu option Settings ‣ Options, click on the Rendering tab and select or deselect following checkboxes:
Przyspieszenie renderowania¶
There are two settings that allow you to improve rendering speed. Open the QGIS options dialog using Settings ‣ Options, go to the Rendering tab and select or deselect the following checkboxes:
Mierzenie¶
Measuring works within projected coordinate systems (e.g., UTM) and unprojected data. If the loaded map is defined with a geographic coordinate system (latitude/longitude), the results from line or area measurements will be incorrect. To fix this, you need to set an appropriate map coordinate system (see section Praca z układami współrzędnych). All measuring modules also use the snapping settings from the digitizing module. This is useful, if you want to measure along lines or areas in vector layers.
To select a measuring tool, click on  and select the tool you want
to use.
and select the tool you want
to use.
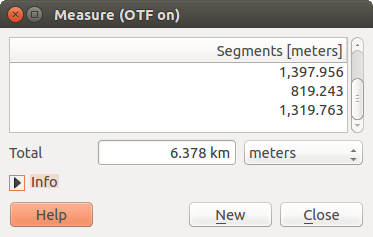
Measure length, areas and angles¶
 Measure Line: QGIS is able to measure real distances
between given points according to a defined ellipsoid. To configure this,
choose menu option Settings ‣ Options, click on the
Map tools tab and select the appropriate ellipsoid. There, you can
also define a rubberband color and your preferred measurement units (meters or
feet) and angle units (degrees, radians and gon). The tool then allows you to
click points on the map. Each segment length, as well as the total, shows up in
the measure window. To stop measuring, click your right mouse button.
Note that you can interactively change the measurement units in the measurement
dialog. It overrides the Preferred measurement units in the options.
There is an info section in the dialog that shows which CRS settings are being used
during measurement calculations.
Measure Line: QGIS is able to measure real distances
between given points according to a defined ellipsoid. To configure this,
choose menu option Settings ‣ Options, click on the
Map tools tab and select the appropriate ellipsoid. There, you can
also define a rubberband color and your preferred measurement units (meters or
feet) and angle units (degrees, radians and gon). The tool then allows you to
click points on the map. Each segment length, as well as the total, shows up in
the measure window. To stop measuring, click your right mouse button.
Note that you can interactively change the measurement units in the measurement
dialog. It overrides the Preferred measurement units in the options.
There is an info section in the dialog that shows which CRS settings are being used
during measurement calculations.
Figure Measure 1:
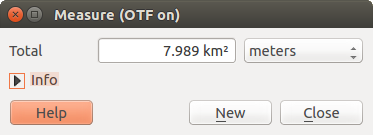
 Measure Area: Areas can also be measured. In the
measure window, the accumulated area size appears. In addition, the measuring
tool will snap to the currently selected layer, provided that layer has its
snapping tolerance set (see section Setting the Snapping Tolerance and Search Radius). So, if you want
to measure exactly along a line feature, or around a polygon feature, first set
its snapping tolerance, then select the layer. Now, when using the measuring
tools, each mouse click (within the tolerance setting) will snap to that layer.
Measure Area: Areas can also be measured. In the
measure window, the accumulated area size appears. In addition, the measuring
tool will snap to the currently selected layer, provided that layer has its
snapping tolerance set (see section Setting the Snapping Tolerance and Search Radius). So, if you want
to measure exactly along a line feature, or around a polygon feature, first set
its snapping tolerance, then select the layer. Now, when using the measuring
tools, each mouse click (within the tolerance setting) will snap to that layer.
Figure Measure 2:
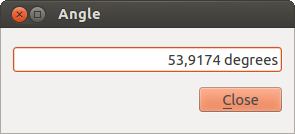
 Measure Angle: You can also measure angles. The
cursor becomes cross-shaped. Click to draw the first segment of the angle you
wish to measure, then move the cursor to draw the desired angle. The measure
is displayed in a pop-up dialog.
Measure Angle: You can also measure angles. The
cursor becomes cross-shaped. Click to draw the first segment of the angle you
wish to measure, then move the cursor to draw the desired angle. The measure
is displayed in a pop-up dialog.
Figure Measure 3:
Zaznaczanie i odznaczanie obiektów¶
The QGIS toolbar provides several tools to select features in the map canvas.
To select one or several features, just click on  and select your
tool:
and select your
tool:
 Select Single Feature
Select Single Feature Select Features by Rectangle
Select Features by Rectangle Select Features by Polygon
Select Features by Polygon Select Features by Freehand
Select Features by Freehand Select Features by Radius
Select Features by Radius
To deselect all selected features click on  Deselect
features from all layers.
Deselect
features from all layers.
![]() Select feature using an expression allow user
to select feature using expression dialog. See Expressions
chapter for some example.
Select feature using an expression allow user
to select feature using expression dialog. See Expressions
chapter for some example.
Users can save features selection into a New Memory Vector Layer or a New Vector Layer using Edit ‣ Paste Feature as ... and choose the mode you want.
Informacje o obiekcie¶
The Identify tool allows you to interact with the map canvas and get information on features
in a pop-up window. To identify features, use View ‣ Identify
features or press Ctrl + Shift + I, or click on the  Identify features icon in the toolbar.
Identify features icon in the toolbar.
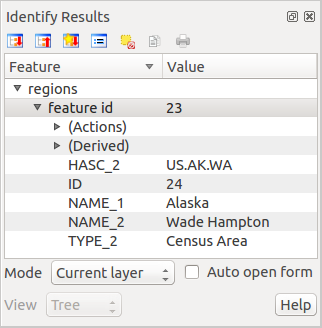
If you click on several features, the Identify results dialog will list information about all the selected features. The first item is the number of the layer in the list of results, followed by the layer name. Then, its first child will be the name of a field with its value. The first field is the one selected in Properties ‣ Display. Finally, all information about the feature is displayed.
Zawartość tego okna można dostosować tak, aby wyświetlały się wybrane pola, ale domyślnie pokazuje ono trzy typy informacji:
- Actions: Actions can be added to the identify feature windows. When clicking on the action label, action will be run. By default, only one action is added, to view feature form for editing.
- Derived: This information is calculated or derived from other information. You can find clicked coordinate, X and Y coordinates, area in map units and perimeter in map units for polygons, length in map units for lines and feature ids.
- Data attributes: This is the list of attribute fields from the data.
Figure Identify 1:
At the top of the window, you have five icons:
At the bottom of the window, you have the Mode and View comboboxes. With the Mode combobox you can define the identify mode: ‘Current layer’, ‘Top down, stop at first’, ‘Top down’ and ‘Layer selection’. The View can be set as ‘Tree’, ‘Table’ and ‘Graph’.
The identify tool allows you to auto open a form. In this mode you can change the feautures attributes.
Inne funkcje można znaleźć w menu kontekstowym rozpoznawanego obiektu. Można, na przykład, wykonać następujące zadania:
Wyświetl formularz obiektu
Zbliż do obiektu
Kopiuj obiekt: skopiuj cały obiekt, tj. jego geometrię i atrybuty;
- Toggle feature selection: adds identified feature to selection
Kopiuj wartość atrybutu: kopiuje wartość klikniętego atrybutu
- Copy feature attributes: Copy only attributes
Wyczyść wyniki: usuwa wyniki z okna
Wyczyść zaznaczenie: usuwane jest zaznaczenie obiektów na mapie
Zaznacz wszystkie
Zaznacz warstwę
Aktywuj warstwę: warstwa obiektu jest aktywowana
Właściwości warstwy: otwiera okno właściwości warstwy
Rozwiń wszystkie
Zwiń wszystkie
Dekoracje¶
The Decorations of QGIS include the Grid, the Copyright Label, the North Arrow and the Scale Bar. They are used to ‘decorate’ the map by adding cartographic elements.
Siatka¶
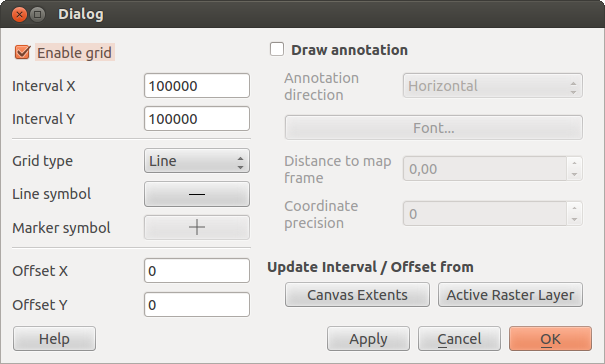
 Siatka pozwala na dodanie do obszaru mapy siatki współrzędnych i jej opisu.
Siatka pozwala na dodanie do obszaru mapy siatki współrzędnych i jej opisu.
Figure Decorations 1:
Z menu Widok ‣ Dekoracje ‣ Siatka. Wyświetli się okno (zob. figure_decorations_1).
Zaznacz pole wyboru
 Siatka i ustaw parametry siatki odpowiednie dla załadowanych do obszaru mapy warstw.
Siatka i ustaw parametry siatki odpowiednie dla załadowanych do obszaru mapy warstw.Zaznacz pole wyboru
 Opisy współrzędnych i ustaw parametry opisu odpowiednie dla załadowanych do obszaru mapy warstw.
Opisy współrzędnych i ustaw parametry opisu odpowiednie dla załadowanych do obszaru mapy warstw.- Click [Apply] to verify that it looks as expected.
- Click [OK] to close the dialog.
Informacja o prawach autorskich¶
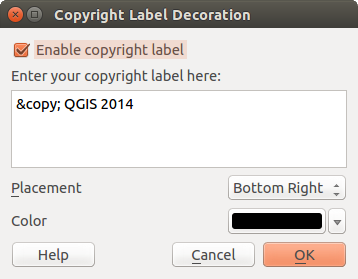
 Copyright label adds a copyright label using the text
you prefer to the map.
Copyright label adds a copyright label using the text
you prefer to the map.
Figure Decorations 2:
Wybierz polecenie Wisok ‣ Dekoracje ‣ Informacje o prawach autorskich. Pokaże się okno (zob. figure_decorations_2).
Wprowadź tekst, który chcesz zamieścić na mapie. Możesz wykorzystać HTML, jak to pokazano w przykładzie.
- Choose the placement of the label from the Placement
 combo box.
combo box. Upewnij się, czy pole wyboru
 Włącz etykietę jest zaznaczone.
Włącz etykietę jest zaznaczone.- Click [OK].
In the example above, which is the default, QGIS places a copyright symbol followed by the date in the lower right-hand corner of the map canvas.
Strzałka północy¶
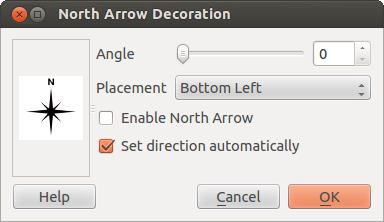
 North Arrow places a simple north arrow on the map canvas.
At present, there is only one style available. You can adjust the angle of the
arrow or let QGIS set the direction automatically. If you choose to let QGIS
determine the direction, it makes its best guess as to how the arrow should be
oriented. For placement of the arrow, you have four options, corresponding to
the four corners of the map canvas.
North Arrow places a simple north arrow on the map canvas.
At present, there is only one style available. You can adjust the angle of the
arrow or let QGIS set the direction automatically. If you choose to let QGIS
determine the direction, it makes its best guess as to how the arrow should be
oriented. For placement of the arrow, you have four options, corresponding to
the four corners of the map canvas.
Figure Decorations 3:
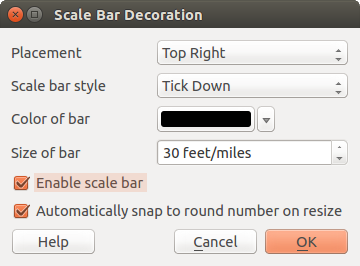
Podziałka¶
 Scale Bar adds a simple scale bar to the map canvas. You
can control the style and placement, as well as the labeling of the bar.
Scale Bar adds a simple scale bar to the map canvas. You
can control the style and placement, as well as the labeling of the bar.
Figure Decorations 4:
QGIS only supports displaying the scale in the same units as your map frame. So if the units of your layers are in meters, you can’t create a scale bar in feet. Likewise, if you are using decimal degrees, you can’t create a scale bar to display distance in meters.
W celu dodania podziałki:
Wybierz polecenie Widok ‣ Dekoracje ‣ Podziałka. Pokaże się okno (zob. figure_decorations_4).
- Choose the placement from the Placement
 combo box.
combo box. - Choose the style from the Scale bar style
 combo box.
combo box. - Select the color for the bar Color of bar
 or use
the default black color.
or use
the default black color. - Set the size of the bar and its label Size of bar
 .
. - Optionally, check
 Automatically snap to round number
on resize.
Automatically snap to round number
on resize. - Click [OK].
Wskazówka
Ustawienia dekoracji
W czasie zapisu projektu .qgs zapisywane są wszystkie zmiany, jakich dokonałeś w siatce, strzałce północy, podziałce i prawach autorskich i będą one użyte, gdy otworzysz ten projekt następnym razem.
Narzędzia opisu¶
The  Text Annotation tool in the attribute
toolbar provides the possibility to place formatted text in a balloon on the
QGIS map canvas. Use the Text Annotation tool and click into the
map canvas.
Text Annotation tool in the attribute
toolbar provides the possibility to place formatted text in a balloon on the
QGIS map canvas. Use the Text Annotation tool and click into the
map canvas.
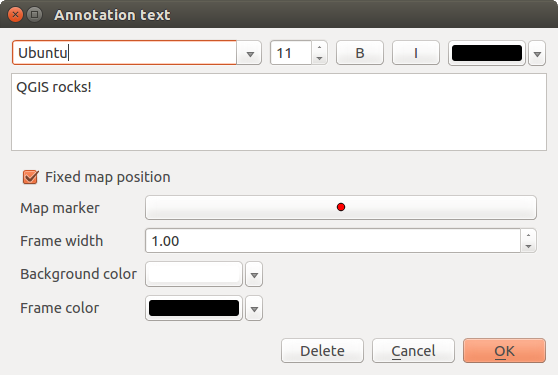
Figure annotation 1:
Dwuklik na wybranym opisie spowoduje otwarcie okna dialogowego z różnymi opcjami. Mamy tu pole edytora tekstowego do wprowadzenia sformatowanego tekstu i inne ustawienia. Jest np. możliwość umiejscowienia opisu w określonej pozycji mapy (wyświetlany jako znacznik) lub utrzymania pozycji opisu na ekranie (niezależnie od mapy). Opis może być przesuwany przez zmianę jego pozycji na mapie (przeciągnij znacznik) lub poprzez przesunięcie samej chmurki. Ikonki są częścią szablonu GIS i są domyślnie używane również w innych szablonach.
The  Move Annotation tool allows you to move the
annotation on the map canvas.
Move Annotation tool allows you to move the
annotation on the map canvas.
Opis HTML¶
The  Html Annotation tools in the attribute
toolbar provides the possibility to place the content of an html file in a
balloon on the QGIS map canvas. Using the Html Annotation tool, click
into the map canvas and add the path to the html file into the dialog.
Html Annotation tools in the attribute
toolbar provides the possibility to place the content of an html file in a
balloon on the QGIS map canvas. Using the Html Annotation tool, click
into the map canvas and add the path to the html file into the dialog.
Opis SVG¶
The  SVG Annotation tool in the attribute toolbar
provides the possibility to place an SVG symbol in a balloon on the QGIS map
canvas. Using the SVG Annotation tool, click into the map canvas and
add the path to the SVG file into the dialog.
SVG Annotation tool in the attribute toolbar
provides the possibility to place an SVG symbol in a balloon on the QGIS map
canvas. Using the SVG Annotation tool, click into the map canvas and
add the path to the SVG file into the dialog.
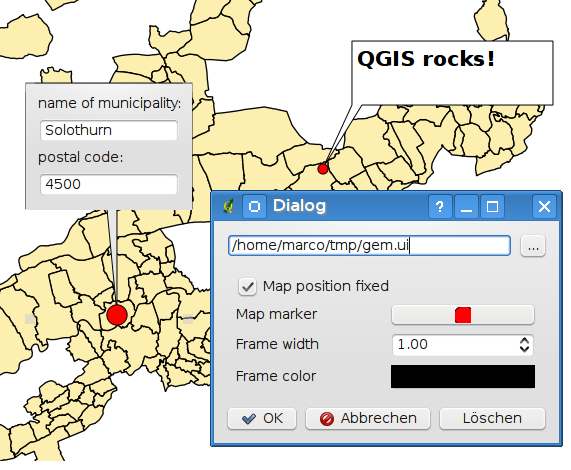
Opisy w formularzu¶
Additionally, you can also create your own annotation forms. The
 Form Annotation tool is useful to display
attributes of a vector layer in a customized Qt Designer form (see
figure_custom_annotation). This is similar to the designer forms for the
Identify features tool, but displayed in an annotation item.
Also see this video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0pDBuSbQ02o from
Tim Sutton for more information.
Form Annotation tool is useful to display
attributes of a vector layer in a customized Qt Designer form (see
figure_custom_annotation). This is similar to the designer forms for the
Identify features tool, but displayed in an annotation item.
Also see this video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0pDBuSbQ02o from
Tim Sutton for more information.
Figure annotation 2:
Informacja
Naciśnięcie kombinacji klawiszy Ctrl+T gdy aktywne jest którekolwiek narzędzie Opisu (przesuń opis, opis tekstowy, opis w formularzu) spowoduje zmianę stanu widoczności opisów.
Zakładki przestrzenne¶
Spatial Bookmarks allow you to “bookmark” a geographic location and return to it later.
Tworzenie zakładki¶
Żeby utworzyć zakładkę:
Zbliż się lub przesuń widok do interesującego Cię obszaru.
- Select the menu option View ‣ New Bookmark or press
Ctrl-B. Wprowadź nazwę zakładki opisującą bieżącą pozycję (może zawierać do 255 znaków).
- Press
Enterto add the bookmark or [Delete] to remove the bookmark.
Zwróć uwagę na to, że możesz mieć wiele zakładek o takiej samej nazwie.
Praca z zakładkami¶
To use or manage bookmarks, select the menu option View ‣ Show Bookmarks. The Geospatial Bookmarks dialog allows you to zoom to or delete a bookmark. You cannot edit the bookmark name or coordinates.
Zooming to a Bookmark¶
From the Geospatial Bookmarks dialog, select the desired bookmark by clicking on it, then click [Zoom To]. You can also zoom to a bookmark by double-clicking on it.
Deleting a Bookmark¶
To delete a bookmark from the Geospatial Bookmarks dialog, click on it, then click [Delete]. Confirm your choice by clicking [Yes], or cancel the delete by clicking [No].
Import or export a bookmark¶
To share or transfer your bookmarks between computers you can use the Share pull down menu in the Geospatial Bookmarks dialog.
Zagnieżdżanie projektów¶
Jeśli w bieżącym projekcie chcesz wykorzystać zawartość innych projektów, możesz wykorzystać polecenie Warstwa ‣ Osadź inny projekt.
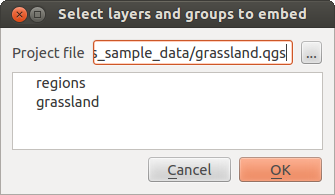
Osadzanie warstw¶
Poniższe okno dialogowe umożliwia osadzenie warstw z innego projektu.
- Press
 to look for another project from the Alaska dataset.
to look for another project from the Alaska dataset. - Select the project file
grassland. You can see the content of the project (see figure_embed_dialog). - Press
Ctrland click on the layersgrasslandandregions. Press [OK]. The selected layers are embedded in the map legend and the map view now.
Figure Nesting 1:
Chociaż osadzone warstwy są edytowalne, nie można zmienić ich właściwości stylu i etykietowania.