GPS Plugin¶
Was ist GPS?¶
GPS, the Global Positioning System, is a satellite-based system that allows anyone with a GPS receiver to find their exact position anywhere in the world. It is used as an aid in navigation, for example in airplanes, in boats and by hikers. The GPS receiver uses the signals from the satellites to calculate its latitude, longitude and (sometimes) elevation. Most receivers also have the capability to store locations (known as waypoints), sequences of locations that make up a planned route and a tracklog or track of the receivers movement over time. Waypoints, routes and tracks are the three basic feature types in GPS data. QGIS displays waypoints in point layers while routes and tracks are displayed in linestring layers.
GPS-Daten aus einer Datei laden¶
There are dozens of different file formats for storing GPS data. The format that QGIS uses is called GPX (GPS eXchange format), which is a standard interchange format that can contain any number of waypoints, routes and tracks in the same file.
Um eine GPX-Datei zu laden, müssen Sie das Plugin ‘GPS Werkzeuge’ über das Menü Erweiterungen  Erweiterungen verwalten ... aktivieren. Aktivieren Sie im QGIS Erweiterungsmanager das Kontrollkästchen von
Erweiterungen verwalten ... aktivieren. Aktivieren Sie im QGIS Erweiterungsmanager das Kontrollkästchen von  GPS Werkzeuge.Wenn dieses Plugin geladen ist erscheinen zwei Knöpfe mit einem kleinen GPS Handgerät in der Werkzeugleiste:
GPS Werkzeuge.Wenn dieses Plugin geladen ist erscheinen zwei Knöpfe mit einem kleinen GPS Handgerät in der Werkzeugleiste:
For working with GPS data we provide an example GPX file available in the QGIS sample dataset: qgis_sample_data/gps/national_monuments.gpx. See Section Beispieldaten for more information about the sample data.
- Select Vector ‣ GPS ‣ GPS Tools or click the
 GPS Tools icon in the toolbar and open the
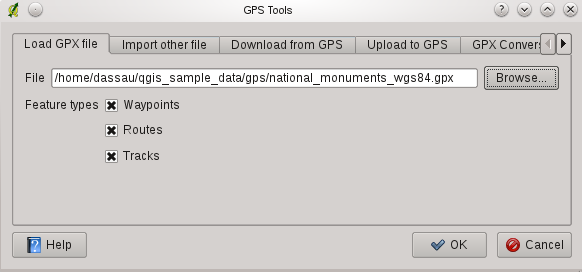
Load GPX file tab (see figure_GPS_1).
GPS Tools icon in the toolbar and open the
Load GPX file tab (see figure_GPS_1). Suchen Sie den Ordner qgis_sample_data/gps/, wählen Sie die GPX-Datei national_monuments.gpx und klicken Sie [Öffnen].
Figure GPS 1:
Verwenden Sie den [Suchen...] Knopf um die GPX-Datei auszuwählen, verwenden Sie dann die Kontrollkästchen um die Objekttypen die aus der GPX-Datei geladen werden sollen auszuwählen. Jeder Objekttyp wird in einen separaten Layer geladen wenn Sie [OK] klicken. Die Datei national_monuments.gpx enthält nur Wegpunkte.
Bemerkung
GPS units allow to store data in different coordinate systems. When downloading a GPX file (from your GPS unit or a web site) and then loading it in QGIS, be sure that the data stored in the GPX file uses WGS84 (latitude/longitude). QGIS expects this and it is the official GPX specification. See http://www.topografix.com/GPX/1/1/
GPSBabel¶
Since QGIS uses GPX files you need a way to convert other GPS file formats to GPX. This can be done for many formats using the free program GPSBabel, which is available at http://www.gpsbabel.org. This program can also transfer GPS data between your computer and a GPS device. QGIS uses GPSBabel to do these things, so it is recommended that you install it. However, if you just want to load GPS data from GPX files you will not need it. Version 1.2.3 of GPSBabel is known to work with QGIS, but you should be able to use later versions without any problems.
GPS-Daten importieren¶
Um GPS-Daten aus einer Datei, die nicht im GPX-Format vorliegt zu importieren, benutzen Sie den Reiter Aus anderer Datei importieren.Wählen Sie dann die Datei (und den Dateityp), die importiert werden soll aus, von welchem Datenformat Sie importieren möchten und wo die konvertierte GPX-Datei unter welchem Namen abgelegt werden soll. Beachten Sie, dass nicht für alle Datenformate die drei GPS-Datentypen Wegpunkte, Routen und Spuren unterstützt werden. Manchmal sind es nur ein oder zwei.
GPS-Daten von einem Empfänger herunterladen¶
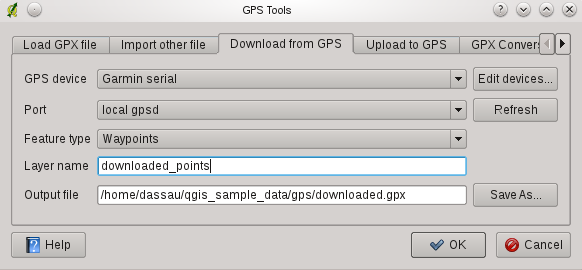
QGIS can use GPSBabel to download data from a GPS device directly as new vector layers. For this we use the Download from GPS tab of the GPS Tools dialog (see Figure_GPS_2). Here, we select the type of GPS device, the port that it is connected to (or usb if your GPS supports this), the feature type that you want to download, the GPX file where the data should be stored, and the name of the new layer.
Figure GPS 2:
Durch die Angabe des Typs Ihres GPS-Empfängers legen Sie fest, wie GPSBabel mit dem Gerät kommuniziert. Wenn kein vorhandener Typ mit Ihrem Empfänger funktioniert, können Sie einen eigenen, neuen Gerätetyp erstellen (vgl. Abschnitt Neues GPS-Gerät definieren).
Der Verbindungsport ist ein Dateiname oder ein anderer Name, den Ihr System als Referenz für den physischen Port benutzt, über den eine Verbindung zum GPS-Empfänger hergestellt wird. Es kann auch einfach USB sein, wenn dies von dem GPS-Gerät unterstützt wird.
When you click [OK] the data will be downloaded from the device and appear as a layer in QGIS.
GPS-Daten auf einen Empfänger hochladen¶
You can also upload data directly from a vector layer in QGIS to a GPS device using the Upload to GPS tab of the GPS Tools dialog. To do this you simply select the layer that you want to upload (which must be a GPX layer), your GPS device type, and the port (or usb) that it is connected to. Just as with the download tool you can specify new device types if your device isn’t in the list.
This tool is very useful in combination with the vector editing capabilities of QGIS. It allows you to load a map, create waypoints and routes, and then upload them and use them on your GPS device.
Neues GPS-Gerät definieren¶
There are lots of different types of GPS devices. The QGIS developers can’t test all of them, so if you have one that does not work with any of the device types listed in the Download from GPS and Upload to GPS tools you can define your own device type for it. You do this by using the GPS device editor, which you start by clicking the [Edit devices] button in the download or the upload tabs.
To define a new device you simply click the [New device] button, enter a name, a download command and an upload command for your device, and click the [Update device] button. The name will be listed in the device menus in the upload and download windows, and can be any string. The download command is the command that is used to download data from the device to a GPX file. This will probably be a GPSBabel command, but you can use any other command line program that can create a GPX file. QGIS will replace the keywords %type, %in, and %out when it runs the command.
%type wird ersetzt durch -w, wenn Sie Wegpunkte herunterladen, -r wenn es eine Route ist und -t, wenn es sich um Spuren handelt. GPSBabel erfährt dadurch, um welchen GPS-Datentyp es sich handelt.
%in will be replaced by the port name that you choose in the download window and %out will be replaced by the name you choose for the GPX file that the downloaded data should be stored in. So if you create a device type with the download command gpsbabel %type -i garmin -o gpx %in %out (this is actually the download command for the predefined device type ‘Garmin serial’) and then use it to download waypoints from port /dev/ttyS0 to the file output.gpx, QGIS will replace the keywords and run the command gpsbabel -w -i garmin -o gpx /dev/ttyS0 output.gpx.
Das Kommando hinaufladen wird benutzt, um die Daten auf Ihren GPS-Empfänger zu transferieren. Es werden dazu die gleichen Schlüsselworte benutzt, nur dass %in durch den Namen der hochzuladenen GPX-Datei und %out durch den Namen des Verbindungsports ersetzt wird.
Sie können mehr über GPSBabel und seine Funktionen unter der URL http://www.gpsbabel.org erlernen.
Wenn Sie einmal einen eigenen Gerätetypen erstellt haben, wird dieser in der Liste der GPS-Geräte dauerhaft angezeigt werden.