General Tools¶
Identify features¶
Identify features allow to interact with map canvas to get data attribut on a
pop-up windows. To identify feature use View ‣ Identify features
or Ctrl+Shift+I, or click on the  Identify features icon
in the toolbar.
Identify features icon
in the toolbar.
If you click on several feature, this pop-up will list all data attributes of all features. The first item is the number of the item in the list of result followed by layer name. Then its first child will be the name of a field with its value. Finally all informations of the feature is displayed.
This window can be customized to display custom fields but by default it will display three kind of information:
- Actions: actions can be added to the identify feature windows. When clicking on the action label, action will be run. By default only one action is added to View feature form for editing.
- Derived: those informations are calculated or derived from other information. You can find clicked coordinate, X and Y coordinates, area in map unit and perimeter in map unit for polygon, length in map unit for line and feature id.
- Data attributes: this is the list of attribute fields from data.
Figure Identify 1:
At the bottom of the windows, you have five icons:
More feature can be found in the menu display with a right click of the mouse somewhere in the response tree.
This menu allows to:
- View Feature form
- Zoom to feature
- Copy feature: copy all feature ie geometry and attributes;
- Copy attribute value: copy only the value of the attribut you click on;
- Copy feature attributes: copy only attributes;
- Clear result: result in the window are removed
- Clear highlights: features highlight on the map are removed
- Highlight all
- Highlight layer
- Layer properties: open layer properties window
- Expand all
- Collapse all
Keyboard shortcuts¶
QGIS provides default keyboard shortcuts for many features. You find them in Section Menu Bar. Additionally the menu option Settings ‣ Configure Shortcuts allows to change the default keyboard shortcuts and to add new keyboard shortcuts to QGIS features.
Figure Shortcuts 1:
Configuration is very simple. Just select a feature from the list and click on [Change], [Set none] or [Set default]. Once you have found your configuration, you can save it as XML file and load it to another QGIS installation.
Context help¶
When you need help on a specific topic, you can access context help via the Help button available in most dialogs - please note that third-party plugins can point to dedicated web pages.
Rendering¶
By default, QGIS renders all visible layers whenever the map canvas must be refreshed. The events that trigger a refresh of the map canvas include:
- Adding a layer
- Panning or zooming
- Resizing the QGIS window
- Changing the visibility of a layer or layers
QGIS allows you to control the rendering process in a number of ways.
Scale Dependent Rendering¶
Scale dependent rendering allows you to specify the minimum and maximum
scales at which a layer will be visible. To set scale dependency rendering,
open the Properties dialog by double-clicking on the layer in the
legend. On the General tab, click on the
 Use scale dependent rendering checkbox to activate
the feature then set the minimum and maximum scale values.
.
Use scale dependent rendering checkbox to activate
the feature then set the minimum and maximum scale values.
.
You can determine the scale values by first zooming to the level you want to use and noting the scale value in the QGIS status bar.
Controlling Map Rendering¶
Map rendering can be controlled in the following ways:
Suspending Rendering¶
To suspend rendering, click the  Render checkbox in the
lower right corner of the statusbar. When the
Render checkbox in the
lower right corner of the statusbar. When the  Render
checkbox is not checked, QGIS does not redraw the canvas in response to any of
the events described in Section Rendering. Examples of when you
might want to suspend rendering include:
Render
checkbox is not checked, QGIS does not redraw the canvas in response to any of
the events described in Section Rendering. Examples of when you
might want to suspend rendering include:
- Add many layers and symbolize them prior to drawing
- Add one or more large layers and set scale dependency before drawing
- Add one or more large layers and zoom to a specific view before drawing
- Any combination of the above
Checking the  Render checkbox enables rendering and causes an immediate
refresh of the map canvas.
Render checkbox enables rendering and causes an immediate
refresh of the map canvas.
Setting Layer Add Option¶
You can set an option to always load new layers without drawing them. This
means the layer will be added to the map, but its visibility checkbox in the
legend will be unchecked by default. To set this option, choose
menu option Settings ‣ Options ‣ and click on the
Rendering menu. Uncheck the  By default new layers
added to the map should be displayed checkbox. Any layer added to the map will
be off (invisible) by default.
By default new layers
added to the map should be displayed checkbox. Any layer added to the map will
be off (invisible) by default.
Another option in Settings ‣ Options ‣ Rendering
menu is the  Enable back buffer checkbox. It provides better
graphics performance at the cost of loosing the possibility to cancel rendering and
incremental feature drawing. If it is unchecked, you can set the ‘Number of features
to draw before updating the display’, otherwise it is inactive.
Enable back buffer checkbox. It provides better
graphics performance at the cost of loosing the possibility to cancel rendering and
incremental feature drawing. If it is unchecked, you can set the ‘Number of features
to draw before updating the display’, otherwise it is inactive.
Finally you can activate the  Use render caching where possible
to speed up redraws checkbox.
Use render caching where possible
to speed up redraws checkbox.
Stopping Rendering¶
To stop the map drawing, press the ESC key. This will halt the refresh of the map canvas and leave the map partially drawn. It may take a bit of time between pressing ESC and the time the map drawing is halted.
Bemærk
It is currently not possible to stop rendering - this was disabled in qt4 port because of User Interface (UI) problems and crashes.
Updating the Map Display During Rendering¶
You can set an option to update the map display as features are drawn. By default, QGIS does not display any features for a layer until the entire layer has been rendered. To update the display as features are read from the datastore, choose menu option Settings ‣ Options click on the Rendering menu. Set the feature count to an appropriate value to update the display during rendering. Setting a value of 0 disables update during drawing (this is the default). Setting a value too low will result in poor performance as the map canvas is continually updated during the reading of the features. A suggested value to start with is 500.
Influence Rendering Quality¶
To influence the rendering quality of the map you have 2 options. Choose menu option Settings ‣ Options click on the Rendering menu and select or deselect following checkboxes.
Measuring¶
Measuring works within projected coordinate systems (e.g., UTM) and unprojected data. If the loaded map is defined with a geographic coordinate system (latitude/longitude), the results from line or area measurements will be incorrect. To fix this you need to set an appropriate map coordinate system (See Section Working with Projections). All measuring modules also use the snapping settings from the digitizing module. This is useful, if you want to measure along lines or areas in vector layers.
To select a measure tool click on  and select the tool you want
to use.
and select the tool you want
to use.
Measure length, areas and angles¶
 Measure Line: QGIS is able to measure real distances between given points
according to a defined ellipsoid. To configure this, choose menu option
Settings ‣ Options, click on the Map tools tab and
choose the appropriate ellipsoid. There you can also define a rubberband color
and your preferred measurement units (meters or feet) and angle units (degrees,
radians and gon). The tools then allows you to click points on the map. Each
segment-length as well as the total shows up in the measure-window. To stop
measuring click your right mouse button.
Measure Line: QGIS is able to measure real distances between given points
according to a defined ellipsoid. To configure this, choose menu option
Settings ‣ Options, click on the Map tools tab and
choose the appropriate ellipsoid. There you can also define a rubberband color
and your preferred measurement units (meters or feet) and angle units (degrees,
radians and gon). The tools then allows you to click points on the map. Each
segment-length as well as the total shows up in the measure-window. To stop
measuring click your right mouse button.
Figure Measure 1:
 Measure Area: Areas can also be measured. In the measure window the
accumulated area size appears. In addition, the measuring tool will snap to the
currently selected layer, provided that layer has its snapping tolerance set.
(See Section Setting the Snapping Tolerance and Search Radius). So if you want to measure exactly along
a line feature, or around a polygon feature, first set its snapping tolerance,
then select the layer. Now, when using the measuring tools, each mouse click
(within the tolerance setting) will snap to that layer.
Measure Area: Areas can also be measured. In the measure window the
accumulated area size appears. In addition, the measuring tool will snap to the
currently selected layer, provided that layer has its snapping tolerance set.
(See Section Setting the Snapping Tolerance and Search Radius). So if you want to measure exactly along
a line feature, or around a polygon feature, first set its snapping tolerance,
then select the layer. Now, when using the measuring tools, each mouse click
(within the tolerance setting) will snap to that layer.
Figure Measure 2:
 Measure Angle: You can also measure angles. The cursor
becomes cross-shaped. Click to draw the first segment of the angle you
wish to measure, then move the the cursor to draw the desired angle. The measure
is displayed in a popup dialog.
Measure Angle: You can also measure angles. The cursor
becomes cross-shaped. Click to draw the first segment of the angle you
wish to measure, then move the the cursor to draw the desired angle. The measure
is displayed in a popup dialog.
Figure Measure 3:
Select and deselect features¶
The QGIS toolbar provides several tools to select features in the map canvas.
To select one or several features just click on
 and select your tool:
and select your tool:
 Select Single Feature
Select Single Feature Select Features by Rectangle
Select Features by Rectangle Select Features by Polygon
Select Features by Polygon Select Features by Freehand
Select Features by Freehand Select Features by Radius
Select Features by Radius
To deselect all selected features click on  Deselect
features from all layers.
Deselect
features from all layers.
Decorations¶
The Decorations of QGIS includes the Grid, Copyright Label, the North Arrow and the Scale Bar. They are used to ‘decorate’ the map by adding cartographic elements.
Grid¶
 Grid allows to add a coordinate grid and
coordinate annotations to the map canvas.
Grid allows to add a coordinate grid and
coordinate annotations to the map canvas.
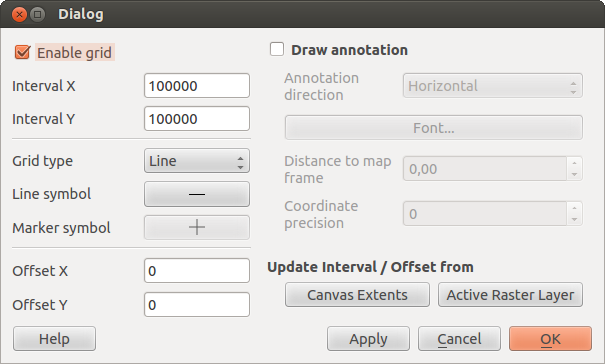
Figure Decorations 1:
- Select from menu View ‣ Decorations ‣ Grid. The dialog starts (see figure_decorations_1).
- Activate the
 Enable grid checkbox and set grid
definitions according to the layers loaded in the map canvas.
Enable grid checkbox and set grid
definitions according to the layers loaded in the map canvas. - Activate the
 Draw annotations checkbox and set
annotation definitions according to the layers loaded in the map canvas.
Draw annotations checkbox and set
annotation definitions according to the layers loaded in the map canvas. - Click [Apply] to check, if it looks as expected.
- Click [OK] to close the dialog.
Copyright Label¶
 Copyright label adds a Copyright label
using the text you prefer to the map.
Copyright label adds a Copyright label
using the text you prefer to the map.
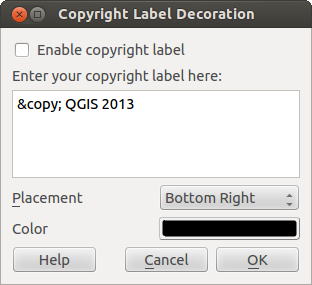
Figure Decorations 2:
- Select from menu View ‣ Decorations ‣ Copyright Label. The dialog starts (see figure_decorations_2).
- Enter the text you want to place on the map. You can use HTML as shown in the example
- Choose the placement of the label from the Placement ‘Bottom Right’ drop-down box
- Make sure the
 Enable Copyright Label checkbox is
checked
Enable Copyright Label checkbox is
checked - Click [OK]
In the example above (default) QGIS places a copyright symbol followed by the date in the lower right hand corner of the map canvas.
North Arrow¶
 North Arrow places a simple north arrow on the
map canvas. At present there is only one style available. You can adjust the
angle of the arrow or let QGIS set the direction automatically. If you choose
to let QGIS determine the direction, it makes its best guess as to how the
arrow should be oriented. For placement of the arrow you have four options,
corresponding to the four corners of the map canvas.
North Arrow places a simple north arrow on the
map canvas. At present there is only one style available. You can adjust the
angle of the arrow or let QGIS set the direction automatically. If you choose
to let QGIS determine the direction, it makes its best guess as to how the
arrow should be oriented. For placement of the arrow you have four options,
corresponding to the four corners of the map canvas.
Figure Decorations 3:
Scale Bar¶
 Scale Bar adds a simple scale bar to the map
canvas. You control the style and placement, as well as the labeling of the bar.
Scale Bar adds a simple scale bar to the map
canvas. You control the style and placement, as well as the labeling of the bar.
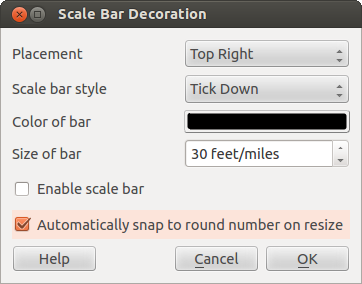
Figure Decorations 4:
QGIS only supports displaying the scale in the same units as your map frame. So if the units of your layers are in meters, you can’t create a scale bar in feet. Likewise if you are using decimal degrees, you can’t create a scale bar to display distance in meters.
To add a scale bar:
- Select from menu View ‣ Decorations ‣ Scale Bar The dialog starts (see figure_decorations_4)
- Choose the placement from the Placement ‘Bottom Left’ drop-down list
- Choose the style from the Scale bar style ‘Tick Down’ list
- Select the color for the bar Color of bar ‘black’ or use the default black color
- Set the size of the bar and its label Size of bar ‘30 degrees’
- Make sure the
 Enable scale bar checkbox is checked
Enable scale bar checkbox is checked - Optionally choose to automatically snap to a round number when the
canvas is resized
 Automatically snap to round number
on resize
Automatically snap to round number
on resize - Click [OK]
Tip
Settings of Decorations
When you save a .qgs project, any changes you have made to Grid, NorthArrow, ScaleBar and Copyright will be saved in the project and restored the next time you load the project.
Annotation Tools¶
The  Text Annotation tools in the attribute toolbar
provides the possibility to place formatted text in a balloon on the QGIS map
canvas. Use the Text Annotation tool and click into the map canvas.
Text Annotation tools in the attribute toolbar
provides the possibility to place formatted text in a balloon on the QGIS map
canvas. Use the Text Annotation tool and click into the map canvas.
Figure annotation 1:
Double click on the item opens a dialog with various options. There is the text editor to enter the formatted text and other item settings. E.g. there is the choice of having the item placed on a map position (displayed by a marker symbol) or to have the item on a screen position (not related to the map). The item can be moved by map position (drag the map marker) or by moving only the balloon. The icons are part of GIS theme, and are used by default in the other themes too.
The  Move Annotation tool allows to move the annotation on the
map canvas.
Move Annotation tool allows to move the annotation on the
map canvas.
Html annotations¶
The  Html Annotation tools in the attribute toolbar
provides the possibility to place the content of a html file in a balloon on the
QGIS map canvas. Use the Html Annotation tool, click into the map
canvas and add the path to the html file into the dialog.
Html Annotation tools in the attribute toolbar
provides the possibility to place the content of a html file in a balloon on the
QGIS map canvas. Use the Html Annotation tool, click into the map
canvas and add the path to the html file into the dialog.
SVG annotations¶
The  SVG Annotation tools in the attribute toolbar
provides the possibility to place a SVG Symbol in a balloon on the QGIS map canvas.
Use the SVG Annotation tool, click into the map canvas and add the
path to the SVG file into the dialog.
SVG Annotation tools in the attribute toolbar
provides the possibility to place a SVG Symbol in a balloon on the QGIS map canvas.
Use the SVG Annotation tool, click into the map canvas and add the
path to the SVG file into the dialog.
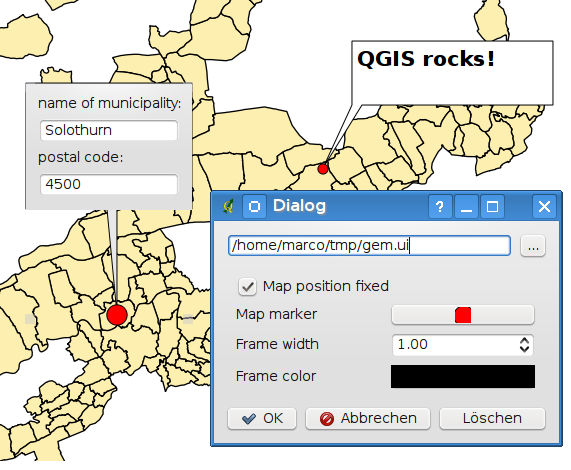
Form annotations¶
Additionally you can also create your own annotation forms. The
 Form Annotation tool is useful to display attributes of
a vector layer in a customized qt designer form (see figure_custom_annotation). It is similar to the
designer forms for the
Identify features tool, but displayed in an annotation item.
Also see QGIS blog http://blog.qgis.org/node/143 for more information.
Form Annotation tool is useful to display attributes of
a vector layer in a customized qt designer form (see figure_custom_annotation). It is similar to the
designer forms for the
Identify features tool, but displayed in an annotation item.
Also see QGIS blog http://blog.qgis.org/node/143 for more information.
Figure annotation 2:
Bemærk
If you press Ctrl+T while an Annotation tool is active (move annotation, text annotation, form annotation), the visibility states of the items are inverted.
Spatial Bookmarks¶
Spatial Bookmarks allow you to “bookmark” a geographic location and return to it later.
Creating a Bookmark¶
To create a bookmark:
- Zoom or pan to the area of interest.
- Select the menu option View ‣ New Bookmark or press Ctrl-B.
- Enter a descriptive name for the bookmark (up to 255 characters).
- Press Enter to add the bookmark or [Delete] to remove the bookmark.
Note that you can have multiple bookmarks with the same name.
Working with Bookmarks¶
To use or manage bookmarks, select the menu option View ‣ Show Bookmarks. The Geospatial Bookmarks dialog allows you to zoom to or delete a bookmark. You can not edit the bookmark name or coordinates.
Zooming to a Bookmark¶
From the Geospatial Bookmarks dialog, select the desired bookmark by clicking on it, then click [Zoom To]. You can also zoom to a bookmark by double-clicking on it.
Deleting a Bookmark¶
To delete a bookmark from the Geospatial Bookmarks dialog, click on it then click [Delete]. Confirm your choice by clicking [Yes] or cancel the delete by clicking [No].
Nesting Projects¶
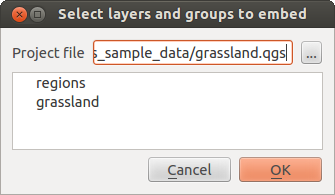
If you want to embed content from other project files into your project you can choose Layer ‣ Embed Layers and Groups.
Embedding layers¶
The following dialog allows you to embed layers from other projects:
- Press
 to look for another project from the Alaska dataset.
to look for another project from the Alaska dataset. - Select the project file grassland. You can see the content of the project (see figure_embed_dialog).
- Press Ctrl and klick on the layers grassland and regions. The layers are embedded in the map legend and the map view now.
Figure Nesting 1:
While the embedded layers are editable you can’t change it’s properties like Style and Labeling.
Removing embedded layers
Add Delimited Text Layer¶
This function allows you to load a delimited text file as a layer in QGIS. Following settings need to be defined:
- The File format usually is
 CSV (comma separated values). If another delimiter is used, activate the
CSV (comma separated values). If another delimiter is used, activate the  custom delimiter radiobutton and if each line in the file is split using a regular expression, please activate the
custom delimiter radiobutton and if each line in the file is split using a regular expression, please activate the  Regular expression delimiter radiobutton.
Regular expression delimiter radiobutton. - As Record options a text file usually provides a delimited header row of field names. This is usually the first line in the text file. If there is no header row available, deactivate the
 first records have field names checkbox. And if the header row isn’t the first line of the text file, define the number of header lines to discard.
first records have field names checkbox. And if the header row isn’t the first line of the text file, define the number of header lines to discard. - As Field options you can trim leading and trailing spaces from fields activating the
 Trim fields checkbox. You can
Trim fields checkbox. You can  Discard empty fields in each record and you can define that the
Discard empty fields in each record and you can define that the  Decimal separator is comma. Otherwise it will be point.
Decimal separator is comma. Otherwise it will be point. - As Geometry definitions a typical text file provides
 Point coordinates. This means there must be an ‘X’ and ‘Y’ field with coordinate values. If the text file provides a
Point coordinates. This means there must be an ‘X’ and ‘Y’ field with coordinate values. If the text file provides a  Well Known Text field, there must be a ‘WKT’ field with geometry information for point, line or polygon objects. These fields can have any name. Otherwise for attribute tables define
Well Known Text field, there must be a ‘WKT’ field with geometry information for point, line or polygon objects. These fields can have any name. Otherwise for attribute tables define  no geometry. The x and y coordinates must be specified as a number. The coordinate system is not important. If they are defined in degree/minutes/seconds, activate the
no geometry. The x and y coordinates must be specified as a number. The coordinate system is not important. If they are defined in degree/minutes/seconds, activate the  DMS coordinates checkbox.
DMS coordinates checkbox. - As Layer settings you can activate
 Use spatial index to improve performance of displaying and spatially selecting features. You can define to
Use spatial index to improve performance of displaying and spatially selecting features. You can define to  Use Subset index and to
Use Subset index and to  Watch file to watch for changes to the file by other applications, while QGIS is running.
Watch file to watch for changes to the file by other applications, while QGIS is running.
As an example of a valid text file we import the elevation point data file elevp.csv coming with the QGIS sample dataset (See Section Sample Data):
X;Y;ELEV
-300120;7689960;13
-654360;7562040;52
1640;7512840;3
[...]
Some items of note about the text file are:
- The example text file uses ; (semicolon) as delimiter. Any character can be used to delimit the fields.
- The first row is the header row. It contains the fields X, Y and ELEV.
- No quotes (") are used to delimit text fields.
- The x coordinates are contained in the X field.
- The y coordinates are contained in the Y field.
Using the function¶
Click the toolbar icon  Add Delimited Text Layer in the
Manage layers toolbar to open the Create a Layer from a
Delimited Text File dialog as shown in figure_delimited_text_1.
Add Delimited Text Layer in the
Manage layers toolbar to open the Create a Layer from a
Delimited Text File dialog as shown in figure_delimited_text_1.
Figure Delimited Text 1:
First select the file (e.g., qgis_sample_data/csv/elevp.csv) to import by clicking on the [Browse] button. Once the file is selected, QGIS attempts to parse the file using the last used delimiter, in this case a semicolon (;). To properly parse the file, it is important to select the correct delimiter. To change the delimiter to tab use \t (this is a regular expression for the tab character).
Once the file is parsed, make a Geometry definition  Point coordinates
and choose the X and Y fields from the dropdown lists. Finally enter a Layer name (e.g., elevp)
as shown in figure_delimited_text_1 . To add the layer to the map, click [OK]. The delimited text file now behaves as
any other map layer in QGIS.
Point coordinates
and choose the X and Y fields from the dropdown lists. Finally enter a Layer name (e.g., elevp)
as shown in figure_delimited_text_1 . To add the layer to the map, click [OK]. The delimited text file now behaves as
any other map layer in QGIS.