4. A configurar e a executar com o QtCreator e QGIS¶
QtCreator é um IDE novo dos criadores da biblioteca Qt. Com o QtCreator, pode criar qualquer projeto C++, mas ele é realmente otimizado para as pessoas que trabalham em aplicações baseadas no Qt (4) (incluindo as aplicações móveis). Tudo o que descrevo em baixo pressupõe que está a executar o Ubuntu 11.04 “Natty”.
4.1. Instalação do QtCreator¶
Esta parte é fácil:
sudo apt-get install qtcreator qtcreator-doc
Depois da instalação deveria encontrá-lo no seu menu gnome
4.2. A configurar o seu projeto¶
I’m assuming you have already got a local QGIS clone containing the source code, and have installed all needed build dependencies etc. There are detailed instructions for git access and dependency installation.
On my system I have checked out the code into $HOME/dev/cpp/QGIS and the
rest of the article is written assuming that, you should update these paths as
appropriate for your local system.
Ao iniciar o QtCreator, faça:
Ficheiro -> Abrir Ficheiro ou Projeto
Then use the resulting file selection dialog to browse to and open this file:
$HOME/dev/cpp/QGIS/CMakeLists.txt
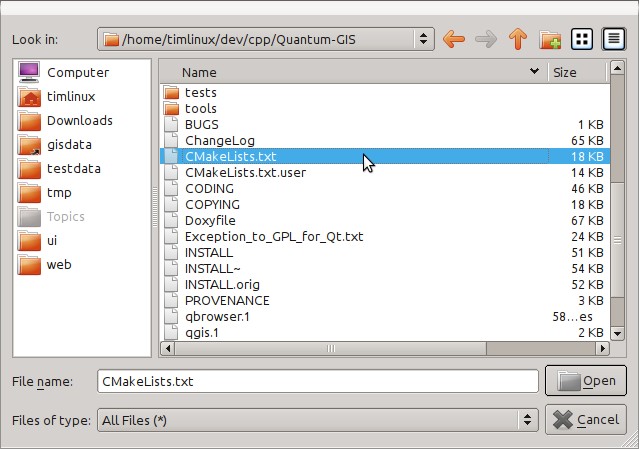
Next you will be prompted for a build location. I create a specific build dir for QtCreator to work in under:
$HOME/dev/cpp/QGIS/build-master-qtcreator
Its probably a good idea to create separate build directories for different branches if you can afford the disk space.
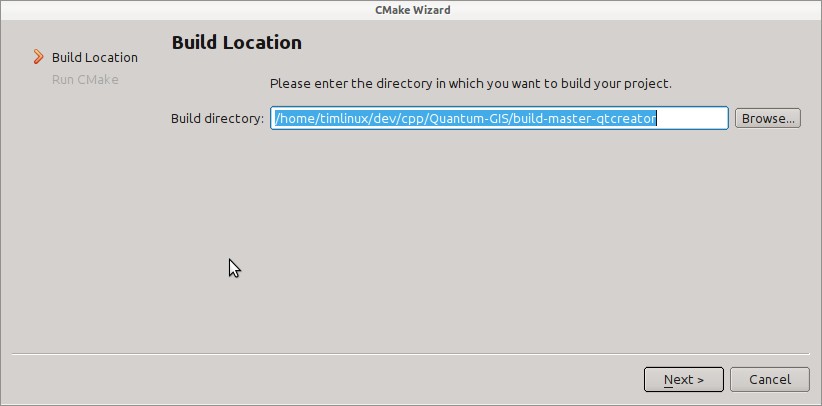
Next you will be asked if you have any CMake build options to pass to CMake. We will tell CMake that we want a debug build by adding this option:
-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Debug
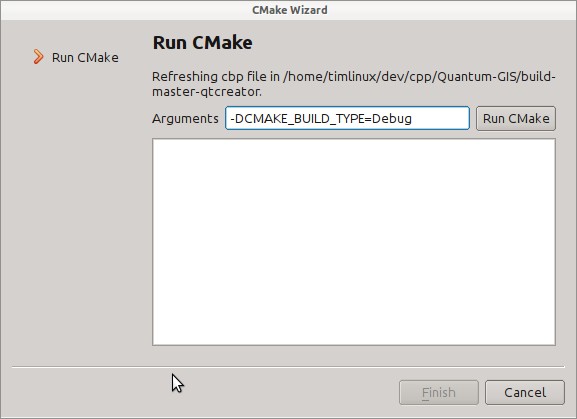
That’s the basics of it. When you complete the Wizard, QtCreator will start scanning the source tree for autocompletion support and do some other housekeeping stuff in the background. We want to tweak a few things before we start to build though.
4.3. A configurar o seu ambiente da compilação¶
Clique mo ícone “Projetos” à esquerda da janela do QtCreator.

Selecione o separador da definições da compilação (normalmente ativo por predefinição).
We now want to add a custom process step. Why? Because QGIS can currently only run from an install directory, not its build directory, so we need to ensure that it is installed whenever we build it. Under “Build Steps”, click on the “Add BuildStep” combo button and choose “Custom Process Step”.
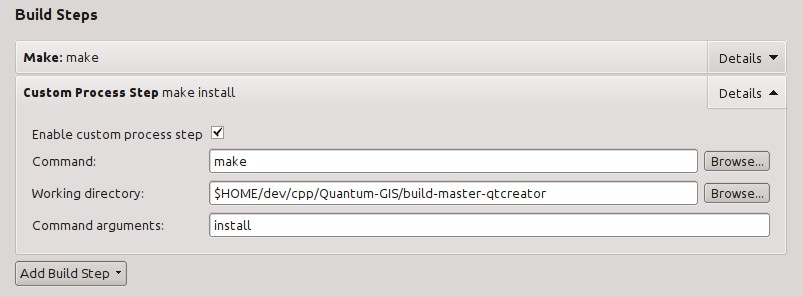
Agora nós definimos os detalhes seguintes:
Ativar passo do processo personalizado: [sim]
Comando «make»
Diretoria de trabalho: $HOME/dev/cpp/QGIS/build-master-qtcreator
Comando argumentos: «install»
You are almost ready to build. Just one note: QtCreator will need write
permissions on the install prefix. By default (which I am using here) QGIS is
going to get installed to /usr/local/. For my purposes on my development
machine, I just gave myself write permissions to the /usr/local directory.
To start the build, click that big hammer icon on the bottom left of the window.

4.4. A configurar o seu ambiente de execução¶
As mentioned above, we cannot run QGIS from directly in the build directly, so
we need to create a custom run target to tell QtCreator to run QGIS from the
install dir (in my case /usr/local/). To do that, return to the projects
configuration screen.

Agora selecione o separador “Definições de Executar”
We need to update the default run settings from using the “qgis” run configuration to using a custom one.
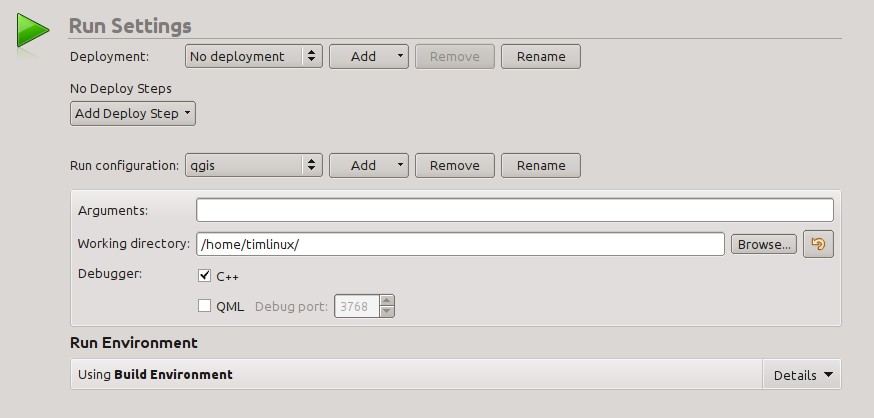
Do do that, click the “Add v” combo button next to the Run configuration combo and choose “Custom Executable” from the top of the list.
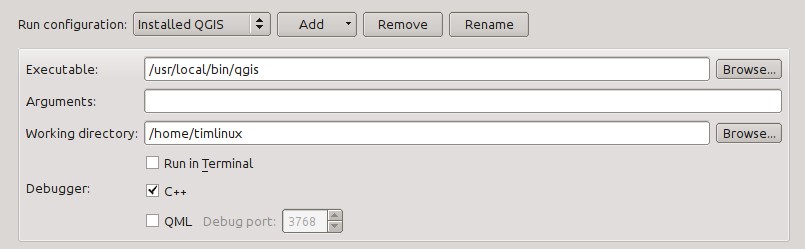
Agora na área das propriedades defina os detalhes seguintes:
Executável: /usr/local/bin/qgis
Argumentos:
Diretoria de trabalho: $HOME
Executar no terminal: [no]
Depurador: C++ [sim]
Qml [não]
Then click the “Rename” button and give your custom executable a meaningful name e.g. “Installed QGIS”
4.5. A executar e a depurar¶
Now you are ready to run and debug QGIS. To set a break point, simply open a source file and click in the left column.
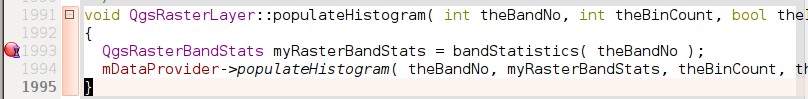
Now launch QGIS under the debugger by clicking the icon with a bug on it in the bottom left of the window.
