14.2. Lesson: Georeferențierea unei Hărți¶
A common forestry task would be the update of the information for a forestry area. It is possible that the previous information for that area dates several years back and was collected analogically (that is, in paper) or perhaps it was digitized but all you have left is the paper version of that inventory data.
Most likely you would like to use that information in your GIS to, for example, compare later with later inventories. This means that you will need to digitize the information at hand using your GIS software. But before you can start the digitizing, there is an important first step to be done, scanning and georeferencing your paper map.
Scopul acestei lecții: De a afla cum să utilizați instrumentul de Georeferențiere din QGIS.
14.2.1.  Scanarea hărții¶
Scanarea hărții¶
The first task you will have to do is to scan your map. If your map is too big, then you can scan it in different parts but keep in mind that you will have to repeat preprocessing and georeferencing tasks for each part. So if possible, scan the map in as few parts as possible.
If you are going to use a different map that the one provided with this manual, use your own scanner to scan the map as an image file, a resolution of 300 DPI will do. If your map has colors, scan the image in color so that you can later use those colors to separate information from your map into different layers (for ex., forest stands, contour lines, roads...).
Pentru acest exercițiu, veți utiliza o hartă scanată anterior, pe care o puteți găsi ca rautjarvi_map.tif în folderul de date exercise_data/forestry
14.2.2.  Follow Along: Georeferențierea hărții scanate¶
Follow Along: Georeferențierea hărții scanate¶
Open QGIS and set the project’s CRS to ETRS89 / ETRS-TM35FIN in Project ‣ Project Properties ‣ CRS, which is the currently used CRS in Finland. Make sure that Enable ‘on the fly’ CRS transformation is checked, since we will be working with old data that is another CRS.
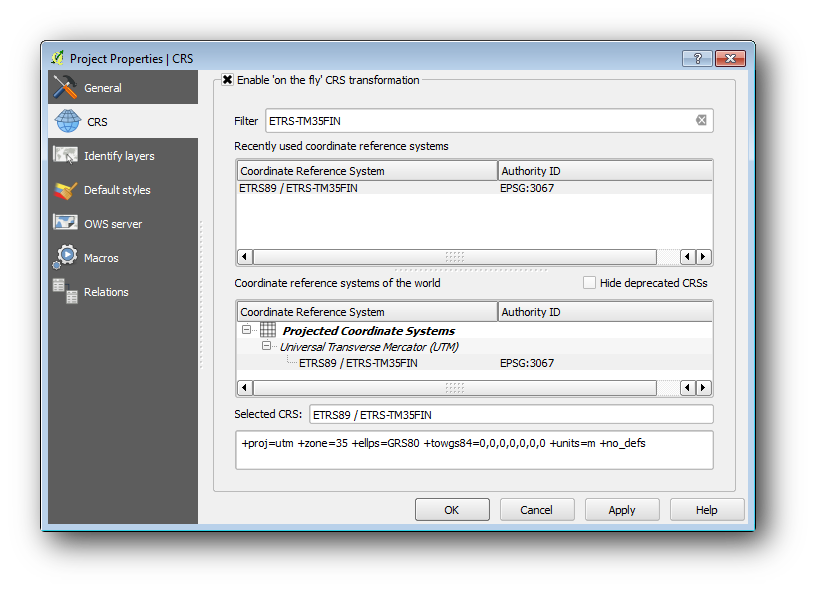
Salvați proiectul QGIS sub numele map_digitizing.qgs.
You will use the georeferencing plugin from QGIS, the plugin is already installed in QGIS. Activate the plugin using the plugin manager as you have done in previous modules. The plugin is named Georeferencer GDAL.
Pentru a georeferenția harta:
Deschideți instrumentul de georeferențiere, Raster ‣ Georeferencer ‣ Georeferencer.
Adăugați fișierul cu imaginea hărții,
rautjarvi_map.tif, ca imagine de georeferențiat, File ‣ Open raster.- When prompted find and select the
KKJ / Finland zone 2CRS, it is the CRS that was used in Finland back in 1994 when this map was created. Clic pe OK
Ulterior ar trebui să definiți setările de transformare pentru georeferențierea hărții:
Deschideți Settings ‣ Transformation settings.
Faceți clic pe pictograma de lângă caseta
Output raster, mergeți și creați folderulexercise_data\forestry\digitizing, apoi denumiți fișierulrautjarvi_georef.tif.Setați restul parametrilor așa cum se arată mai jos.
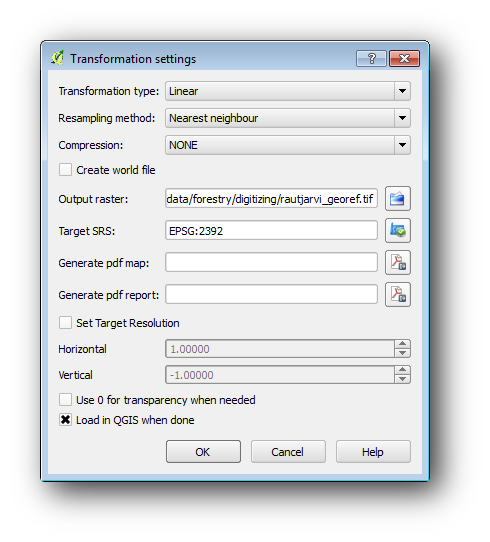
Clic pe OK
The map contains several cross-hairs marking the coordinates in the map, we will use those to georeferenciate this image. You can use the zooming and panning tools as you usually do in QGIS to inspect the image in the Georeferencer’s window.
- Zoom in to the left lower corner of the map and note that there is a cross-hair with a coordinate pair, x and y, that as mentioned before are in
KKJ / Finland zone 2CRS. You will use this point as the first ground control point for the georeferencing your map. Selectați instrumentul Adăugare punct, apoi faceți clic pe intersecția firelor reticulare (deplasați și măriți după nevoie).
În dialogul Enter map coordinates notați coordonatele care apar pe hartă (X: 2557000 si Y: 6786000).
Clic pe OK
Prima coordonată de georeferențiat deja este gata.
Look for other cross-hairs in the black lines image, they are separated 1000 meters from each other both in North and East direction. You should be able to calculate the coordinates of those points in relation to the first one.
Zoom out in the image and move to the right until you find other cross-hair, and estimate how many kilometres you have moved. Try to get ground control points as far from each other as possible. Digitize at least three more ground control points in the same way you did the first one. You should end up with something similar to this:

With already three digitized ground control points you will be able to see the georeferencing error as a red line coming out of the points. The error in pixels can be seen also in the GCP table in the dX[pixels] and dY[pixels] columns. The error in pixels should not be higher than 10 pixels, if it is you should review the points you have digitized and the coordinates you have entered to find what the problem is. You can use the image above as a guide.
O dată ce vă mulțumesc punctele dvs. de control, salva punctele de control de pe teren, în cazul în care veți avea nevoie de ele mai târziu:
- File ‣ Save GCP points as....
În folderul
exercise_data\forestry\digitizing, denumiți fișierulrautjarvi_map.tif.points.
În cele din urmă, georeferențiați harta dvs.:
- File ‣ Start georeferencing.
Rețineți că deja ați denumit fișierul
rautjarvi_georef.tif, când ați editat setările Georeferențiatorului.
Now you can see the map in QGIS project as a georeferenced raster. Note that the raster seems to be slightly rotated, but that is simply because the data is KKJ / Finland zone 2 and your project is in ETRS89 / ETRS-TM35FIN.
To check that your data is properly georeferenced you can open the aerial image in the exercise_data\forestry folder, named rautjarvi_aerial.tif. Your map and this image should match quite well. Set the map transparency to 50% and compare it to the aerial image.

Salvați modificările proiectului QGIS, apoi veți continua din acest punct cu lecția următoare.
14.2.3. In Conclusion¶
După cum ați văzut, georeferențierea unei hărți de hârtie este o operațiune relativ simplă.
14.2.4. What’s Next?¶
În lecția următoare, veți digitiza pâlcurile de pădure din harta dvs. sub formă de poligoane, iar apoi veți adăuga datele de inventar la ele