.
Interpolation Plugin¶
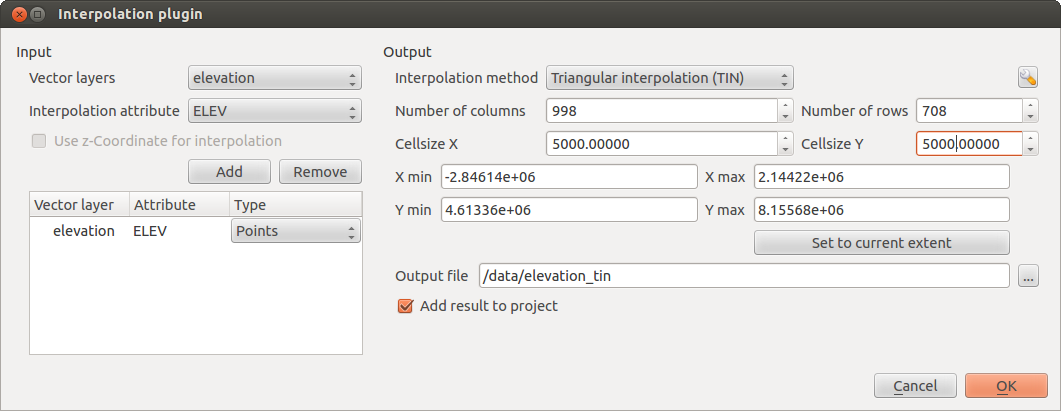
The Interplation plugin can be used to generate a TIN or IDW interpolation of a point vector layer. It is very simple to handle and provides an intuitive graphical user interface for creating interpolated raster layers (see Figure_interpolation_1). The plugin requires the following parameters to be specified before running:
- Input Vector layers: Specify the input point vector layer(s) from a list of
loaded point layers. If several layers are specified, then data from all layers
is used for interpolation. Note: It is possible to insert lines or polygons as
constraints for the triangulation, by specifying either “points”, “structure
lines” or “break lines” in the Type
 combo box.
combo box. - Interpolation attribute: Select the attribute column to be used for interpolation
or enable the
 Use Z-Coordinate checkbox to use the layer’s
stored Z values.
Use Z-Coordinate checkbox to use the layer’s
stored Z values. - Interpolation Method: Select the interpolation method. This can be either ‘Triangulated Irregular Network (TIN)’ or ‘Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW)’.
- Number of columns/rows: Specify the number of rows and columns for the output raster file.
- Output file: Specify a name for the output raster file.
 Add result to project to load the result into the map canvas.
Add result to project to load the result into the map canvas.
Figure Interpolation 1:
Using the plugin¶
- Start QGIS and load a point vector layer (e.g., elevp.csv).
- Load the Interpolation plugin in the Plugin Manager (see
The Plugins Dialog) and click on the Raster ‣ Interpolation ‣
 Interpolation
, which appears in the QGIS menu bar. The Interpolation plugin dialog
appears as shown in Figure_interpolation_1.
Interpolation
, which appears in the QGIS menu bar. The Interpolation plugin dialog
appears as shown in Figure_interpolation_1. - Select an input layer (e.g., elevp
 ) and column
(e.g., ELEV) for interpolation.
) and column
(e.g., ELEV) for interpolation. - Select an interpolation method (e.g., ‘Triangulated Irregular Network (TIN)’), and specify a cell size of 5000 as well as the raster output filename (e.g., elevation_tin).
- Click [OK].