Введение¶
Этот документ задумывался как учебник и справочное пособие. Вы не найдёте здесь описания всех возможных вариантов использования, это скорее обзор основных функциональных возможностей.
Начиная с версии 0.9, в QGIS появилась возможность поддержки сценариев на языке программирования Python. Мы выбрали Python, так как это один из наиболее известных скриптовых языков. Привязки (bindings) PyQGIS зависят от SIP и PyQt4. Основная причина использования SIP вместо более распространенного SWIG состоит в том, что код QGIS зависит от библиотек Qt. Привязки Python к Qt (PyQt) также создаются с использованием SIP, что позволяет обеспечить прозрачную интерграцию PyQGIS и PyQt.
There are several ways how to use Python bindings in QGIS desktop, they are covered in detail in the following sections:
- automatically run Python code when QGIS starts
ввод команд в консоли Python QGIS
создание и использование расширений на Python
создание собственного приложения на базе QGIS API
Python bindings are also available for QGIS Server:
- starting from 2.8 release, Python plugins are also available on QGIS Server (see: Server Python Plugins)
- starting from 2.11 version (Master at 2015-08-11), QGIS Server library has Python bindings that can be used to embed QGIS Server into a Python application.
Существует полное описание QGIS API, в котором собрана информация обо всех классах библиотек QGIS. QGIS Python API практически идентично C++ API.
A good resource when dealing with plugins is to download some plugins from plugin repository and examine their code. Also, the python/plugins/ folder in your QGIS installation contains some plugin that you can use to learn how to develop such plugin and how to perform some of the most common tasks.
Выполнение кода Python при запуске QGIS¶
Существуют два различных метода выполнения кода Python при каждом запуске QGIS.
PYQGIS_STARTUP environment variable¶
You can run Python code just before QGIS initialization completes by setting the PYQGIS_STARTUP environment variable to the path of an existing Python file.
This method is something you will probably rarely need, but worth mentioning here because it is one of the several ways to run Python code within QGIS and because this code will run before QGIS initialization is complete. This method is very useful for cleaning sys.path, which may have undesireable paths, or for isolating/loading the initial environ without requiring a virt env, e.g. homebrew or MacPorts installs on Mac.
The startup.py file¶
Every time QGIS starts, the user’s Python home directory (usually: .qgis2/python) is searched for a file named startup.py, if that file exists, it is executed by the embedded Python interpreter.
Консоль Python¶
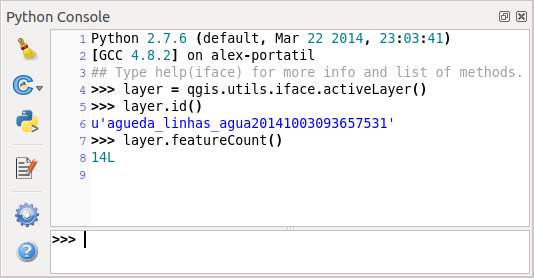
Для небольших сценариев можно воспользоваться встроенной консолью Python. Открыть её можно из меню: Модули ‣ Консоль Python. Консоль откроется как немодальное окно:
The screenshot above illustrates how to get the layer currently selected in the layer list, show its ID and optionally, if it is a vector layer, show the feature count. For interaction with QGIS environment, there is a iface variable, which is an instance of QgsInterface. This interface allows access to the map canvas, menus, toolbars and other parts of the QGIS application.
For convenience of the user, the following statements are executed when the console is started (in future it will be possible to set further initial commands)
from qgis.core import *
import qgis.utils
Тем, кто использует консоль часто, стоит назначить комбинацию клавиш для её вызова (в меню Установки ‣ Комбинации клавиш...)
Расширения на Python¶
QGIS allows enhancement of its functionality using plugins. This was originally possible only with C++ language. With the addition of Python support to QGIS, it is also possible to use plugins written in Python. The main advantage over C++ plugins is its simplicity of distribution (no compiling for each platform needed) and easier development.
Many plugins covering various functionality have been written since the introduction of Python support. The plugin installer allows users to easily fetch, upgrade and remove Python plugins. See the Python Plugin Repositories page for various sources of plugins.
Создание расширений на Python — это просто, см. Разработка расширений на Python.
Примечание
Python plugins are also available in QGIS server (QGIS as OGC Data Server), see QGIS Server Python Plugins for further details.
Приложения на Python¶
При обработке ГИС данных часто удобнее создать несколько сценариев, автоматизирующих процесс, чем постоянно выполнять одни и те же действия. Это более чем возможно при использовании PyQGIS — просто импортируйте модуль qgis.core, инициализируйте его и всё готово к обработке.
Или же вам может потребоваться интерактивное приложение, обладающее некоторым функционалом ГИС — измерение данных, экспорт карты в формат PDF или что-то ещё. Модуль qgis.gui предоставляет различные элементы интерфейса, наиболее важный среди них — виджет карты, который легко интегрируется в приложение и поддерживает масштабирование, панорамирование и/или любые другие инструменты для работы с картой.
PyQGIS custom applications or standalone scripts must be configured to locate the QGIS resources such as projection information, providers for reading vector and raster layers, etc. QGIS Resources are initialized by adding a few lines to the beginning of your application or script. The code to initialize QGIS for custom applications and standalone scripts is similar, but examples of each are provided below.
Примечание: не используйте имя qgis.py для своих сценариев — Python не сможет импортировать привязки, так как имя сценария будет “затенять” их.
Using PyQGIS in standalone scripts¶
To start a standalone script, initialize the QGIS resources at the beginning of the script similar to the following code:
from qgis.core import *
# supply path to qgis install location
QgsApplication.setPrefixPath("/path/to/qgis/installation", True)
# create a reference to the QgsApplication, setting the
# second argument to False disables the GUI
qgs = QgsApplication([], False)
# load providers
qgs.initQgis()
# Write your code here to load some layers, use processing algorithms, etc.
# When your script is complete, call exitQgis() to remove the provider and
# layer registries from memory
qgs.exitQgis()
We begin by importing the qgis.core module and then configuring the prefix path. The prefix path is the location where QGIS is installed on your system. It is configured in the script by calling the setPrefixPath method. The second argument of setPrefixPath is set to True, which controls whether the default paths are used.
The QGIS install path varies by platform; the easiest way to find it for your your system is to use the Консоль Python from within QGIS and look at the output from running QgsApplication.prefixPath().
After the prefix path is configured, we save a reference to QgsApplication in the variable qgs. The second argument is set to False, which indicates that we do not plan to use the GUI since we are writing a standalone script. With the QgsApplication configured, we load the QGIS data providers and layer registry by calling the qgs.initQgis() method. With QGIS initialized, we are ready to write the rest of the script. Finally, we wrap up by calling qgs.exitQgis() to remove the data providers and layer registry from memory.
Using PyQGIS in custom applications¶
The only difference between Using PyQGIS in standalone scripts and a custom PyQGIS application is the second argument when instantiating the QgsApplication. Pass True instead of False to indicate that we plan to use a GUI.
from qgis.core import *
# supply path to qgis install location
QgsApplication.setPrefixPath("/path/to/qgis/installation", True)
# create a reference to the QgsApplication
# setting the second argument to True enables the GUI, which we need to do
# since this is a custom application
qgs = QgsApplication([], True)
# load providers
qgs.initQgis()
# Write your code here to load some layers, use processing algorithms, etc.
# When your script is complete, call exitQgis() to remove the provider and
# layer registries from memory
qgs.exitQgis()
Теперь можно работать с API QGIS — загружать слои, выполнять какую-то обработку или создать графическое приложение с картой. Возможности бесконечны :-)
Запуск приложений¶
Необходимо указать системе где искать библиотеки QGIS и соответствующие модули Python — иначе при запуске появится сообщение об ошибке:
>>> import qgis.core
ImportError: No module named qgis.core
Для этого необходимо установить переменную окружения PYTHONPATH. В приведенных ниже командах qgispath необходимо заменить на реальный путь к каталогу с установленной QGIS:
в Linux: export PYTHONPATH=/qgispath/share/qgis/python
в Windows: set PYTHONPATH=c:\qgispath\python
Теперь путь к модулям PyQGIS известен, но они в свою очередь зависят от библиотек qgis_core и qgis_gui (модули Python служат всего лишь “обёртками” над этими библиотеками). Обычно, операционной системе неизвестно расположение этих библиотек, поэтому вы получите ошибку импорта еще раз (сообщение может отличаться в зависимости от системы):
>>> import qgis.core
ImportError: libqgis_core.so.1.5.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
Проблема решается путем добавления каталогов с библиотеками QGIS в путь поиска линковщика:
в Linux: export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/qgispath/lib
в Windows: set PATH=C:\qgispath;%PATH%
Эти команды можно вписать в загрузочный скрипт, который будет настраивать систему перед запуском приложения. При развертывании приложений, использующих PyQGIS, можно использовать один из двух способов:
требовать от пользователя перед инсталляцией вашего приложения выполнять установку QGIS. Установщик приложения должен выполнять поиск каталогов с библиотеками QGIS и позволять пользователю задать эти каталоги вручную. Преимуществом такого подхода является простота, однако, он требует от пользователя выполнения дополнительных действий.
поставлять QGIS вместе со своим приложением. Подготовка в выпуску станет более сложной и размер приложения возрастет, но зато пользователи будут избавлены от необходимости загружать и устанавливать дополнительное программное обеспечение.
Эти два подхода можно комбинировать — можно развертывать самостоятельное приложение в Windows и Mac OS X, а в Linux оставить установку QGIS на попечении пользователя и пакетного менеджера.