15.3. Lesson: Import and Export¶
Of course, a database with no easy way to migrate data into it and out of it would not be of much use. Fortunately, there are a number of tools that will let you easily move data into and out of PostGIS.
15.3.1. shp2pgsql¶
shp2pgsql is a commandline tool to import ESRI shapefiles to the database. Under Unix, you can use the following command for importing a new PostGIS table:
shp2pgsql -s <SRID> -c -D -I <path to shapefile> <schema>.<table> | \
psql -d <databasename> -h <hostname> -U <username>
Under Windows, you have to perform the import process in two steps:
shp2pgsql -s <SRID> -c -D -I <path to shapefile> <schema>.<table> > import.sql
psql psql -d <databasename> -h <hostname> -U <username> -f import.sql
You may encounter this error:
ERROR: operator class "gist_geometry_ops" does not exist for access method
"gist"
This is a known issue regarding the creation in situ of a spatial index for the data you’re importing. To avoid the error, exclude the -I parameter. This will mean that no spatial index is being created directly, and you’ll need to create it in the database after the data have been imported. (The creation of a spatial index will be covered in the next lesson.)
15.3.2. pgsql2shp¶
pgsql2shp is a commandline tool to export PostGIS Tables, Views or SQL select queries. To do this under Unix:
pgsql2shp -f <path to new shapefile> -g <geometry column name> \
-h <hostname> -U <username> <databasename> <table | view>
To export the data using a query:
pgsql2shp -f <path to new shapefile> -g <geometry column name> \
-h <hostname> -U <username> "<query>"
15.3.3. ogr2ogr¶
ogr2ogr is a very powerful tool to convert data into and from postgis to many data formats. ogr2ogr is part of the GDAL/OGR Software and has to be installed separately. To export a table from PostGIS to GML, you can use this command:
ogr2ogr -f GML export.gml PG:'dbname=<databasename> user=<username>
host=<hostname>' <Name of PostGIS-Table>
15.3.4. SPIT¶
SPIT is a QGIS plugin which is delivered with QGIS. You can use SPIT for uploading ESRI shapefiles to PostGIS.
Once you’ve added the SPIT plugin via the Plugin Manager, look for this button:

Clicking on it or selecting Database –> Spit –> Import Shapefiles to PostgreSQL from the menu will give you the SPIT dialog:
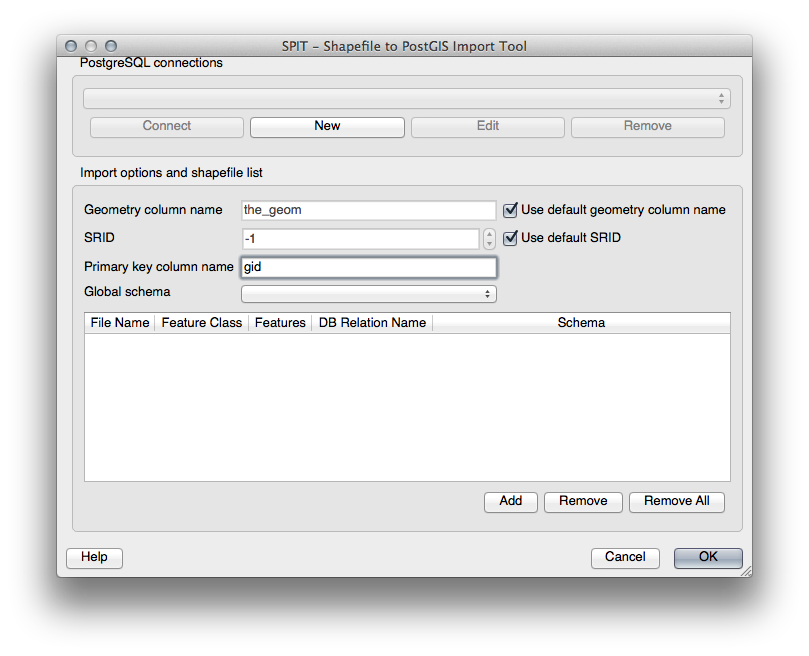
You can add shapefiles to the database by clicking the Add button, which will give you a file browser window.
15.3.5. DB Manager¶
You may have noticed another option in the Database menu labeled DB Manager. This is a new tool in QGIS 2.0 that provides a unified interface for interacting with spatial databases including PostGIS. It also allows you to import and export from databases to other formats. Since the next module is largely devoted to using this tool, we will only briefly mention it here.
15.3.6. In Conclusion¶
Importing and exporting data to and from the database can be done in many various ways. Especially when using disparate data sources, you will probably use these functions (or others like them) on a regular basis.
15.3.7. What’s Next?¶
Next we’ll look at how to query the data we’ve created before.