18.3. Lesson: Working with spatialite databases in QGIS¶
While PostGIS is generally used on a server to provide spatial database capabilities to multiple users at the same time, QGIS also supports the use of a file format called spatialite that is a lightweight, portable way to store an entire spatial database in a single file. Obviously, these 2 types of spatial databases should be used for different purposes, but the same basic principles and techniques apply to both. Let’s create a new spatialite database and explore the functionality provided to work with these databases in QGIS.
The goal for this lesson: To learn how to interact with spatialite databases using the QGIS Browser interface.
18.3.1.  Follow Along: Creating a Spatialite database with the Browser¶
Follow Along: Creating a Spatialite database with the Browser¶
Using the Browser panel, we can create a new spatialite database and get it setup for use in QGIS.
- Right click on the Spatialite entry in the Browser tree and select Create Database.
- Specify where on your filesystem you want to store the file and name it qgis-sl.db.
- Again right click on the Spatialite entry in the Browser tree and now select the New Connection item. Find the file you created in the last step and open it.
Now that you have configured your new database you will find that the entry in Browser tree has nothing underneath it and the only thing you can do at this point is to delete the connection. This is of course because we haven’t added any tables to this database. Let’s go ahead and do that.
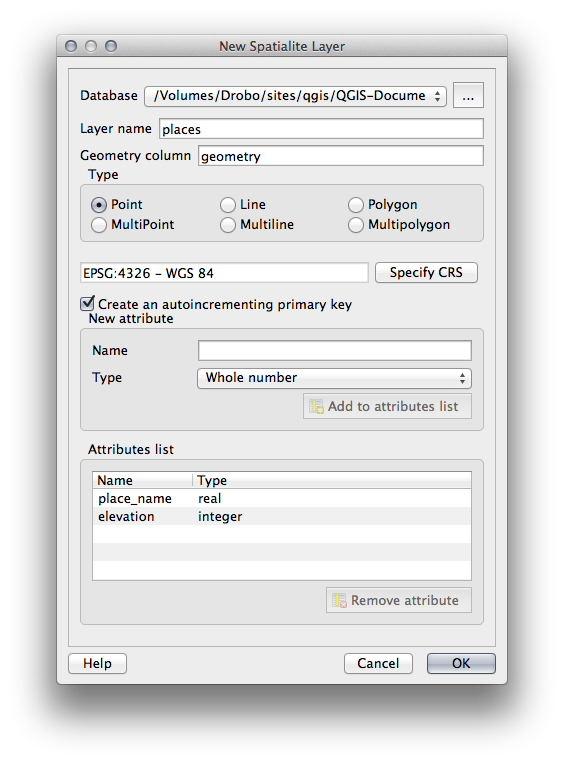
Find the button to create a new layer and use the dropdown to create a new new Spatialite layer, or select Layer –> New –> New Spatialite Layer.
Select the database we created in the previous steps in the drop down.
Give the layer the name places.
Tick the checkbox next to Create an auto-incrementing primary key.
Add 2 attributes as shown in below
Click OK to create the table.
- Click the refresh button at the top of the Browser and you should now see your places table listed.
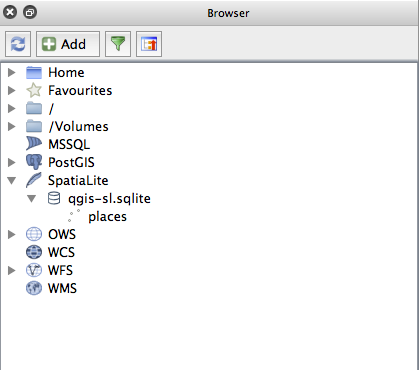
You can right click on the table and view its properties as we did in the previous exercise.
From here you can start an editing session and start adding data to your new database directly.
We also learned about how to import data into a database using the DB Manager and you can use this same technique to import data into your new spatialite DB.
18.3.2. In Conclusion¶
You have seen how to create spatialite databases and add tables to them and to use these tables as layers in QGIS.
